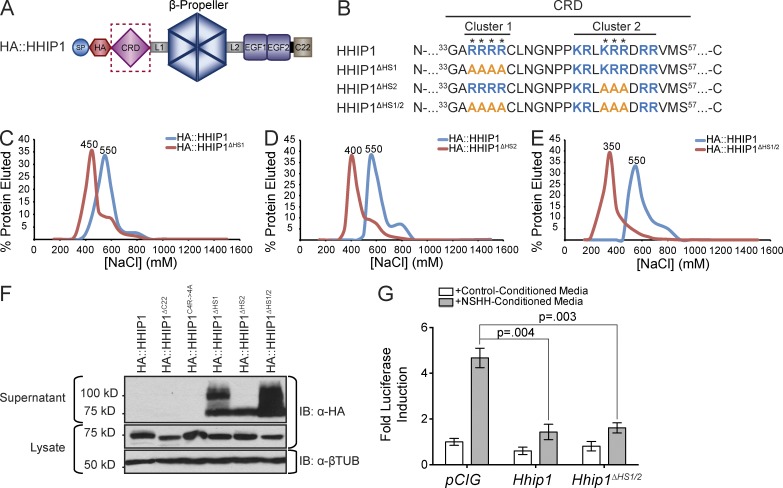
Figure 6.
Identification of specific residues that mediate HS binding and cell surface retention of HHIP1. (A) Cartoon depiction of HA::HHIP1. (B) Sequence analysis identifies two clusters of basic residues (blue) in the CRD that were mutagenized to alanines (orange) to generate HA::HHIP1ΔHS1, HA::HHIP1ΔHS2, and HA::HHIP1ΔHS1/2. (C–E) Heparin binding of HA::HHIP1 (C–E), HA::HHIP1ΔHS1 (C), HA::HHIP1ΔHS2 (D), and HA::HHIP1ΔHS1/2 (E) was assessed by heparin-agarose chromatography. NaCl elution peaks (in millimolars) are indicated above each curve. Representative data are presented from at least three replicates per construct. (F) Immunoblot analysis of COS-7 cell lysates (bottom) and supernatants (top) expressing HA-tagged HHIP1 HS-binding mutants. Of note, in addition to the expected 75-kD HHIP1 band, we also observe the presence of a 100-kD form in some of the HS-binding mutants. IB, immunoblot; βTUB, β-tubulin. (G) HH-responsive luciferase reporter activity measured from NIH/3T3 cells stimulated with either control-conditioned media or NSHH-conditioned media and transfected with the indicated constructs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. P-value is determined by two-tailed Student’s t test.