Fig. 1.
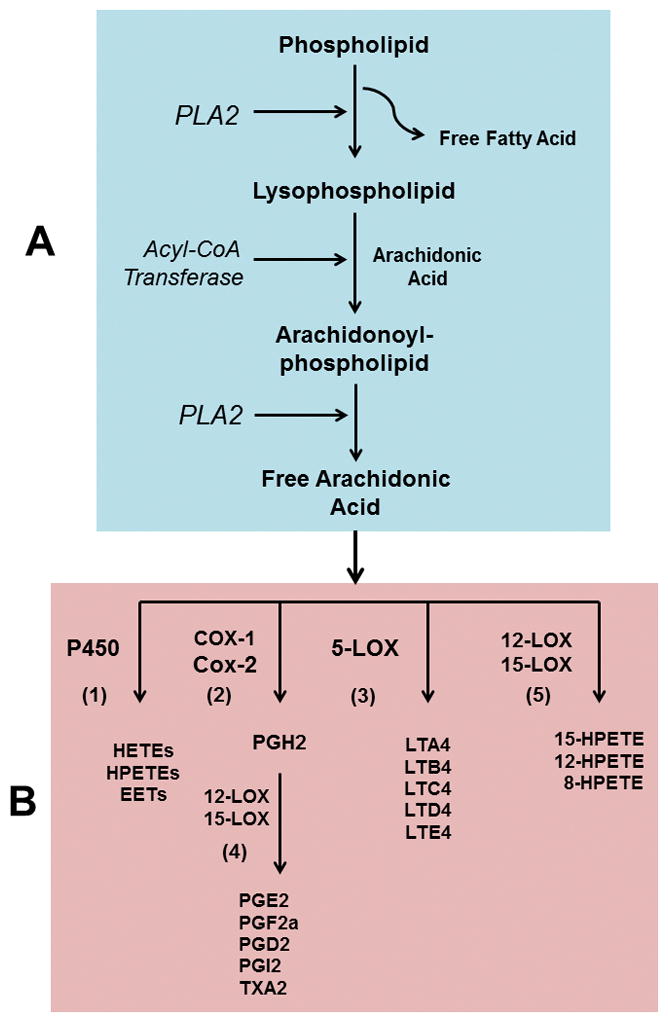
Fatty acid remodeling of membrane phospholipid (compartment A). The existing fatty acids at the SN2 position of a phospholipid is hydrolyzed by PLA2, generating a lysophospholipid molecule. Lysophospholipid serves as an acceptor of a new PUFA (usually arachidonic acid) to synthesize remodeled arachidonoyl-phospholipid catalyzed by acyl-CoA transferase enzymes. In the next step, arachidonoyl-phospholipid undergoes deacylation reaction (by PLA2) releasing free arachidonic acid. Free arachidonic acid acts as a substrate of COX and LOX enzymes of eicosanoid pathway (compartment B) and synthesizes PGs, TXA2, LTs and HETE/HPETE molecules. Compartment B: (1) arachidonic acid can be utilized by cytochrome P450 enzymes to synthesize HETEs, HPETEs and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). (2) COX-1/COX-2 enzymes converts arachidonic acid to PGH2 and then to other PGs facilitated by 12-LOX and 15-LOX as shown in step 4; (3) 5-LOX converts arachidonic acid to various LTs. (5) 15-, 12- and 8-HPETEs are synthesized from arachidonic acid by the help of 12- and 15-LOX enzymes. PLA2, phospholipase A2; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; PG, prostaglandin; TXA2, thromboxane A2, LT, leukotriene; HETE, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids; HPETE, hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids; COX, cycooxygenase; LOX, lipooxygenase.
