Table 2. The relationship between fatty acids composition and stroke severity on admission (National Institute of Health Stroke Scale score)*.
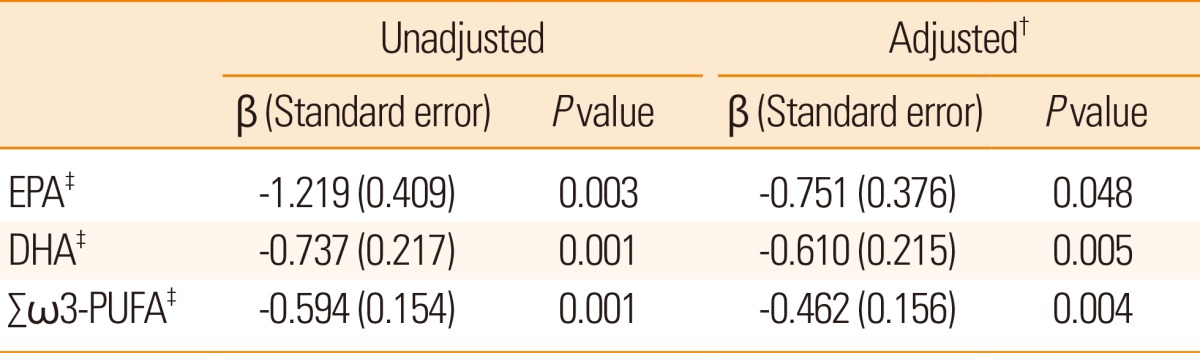
*Linear regression analysis with National Institute of Health Stroke Scale score as dependent and continuous variable; †Adjusted age, sex, and variables with P value < 0.1 in univariate analysis (stroke subtype, hemoglobin, high-density lipoprotein, high sensitivity C-reactive protein, fasting glucose, 16:0 palmitic acid and Σ saturated fatty acids); ‡R2 in multivariate linear regression analysis, when entering EPA: 0.305, DHA: 0.324 and Σ ω3-PUFA: 0.327, respectively.
EPA, 20:5 ω3 eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA, 22:6 ω3 docosahexaenoic acid; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid.
