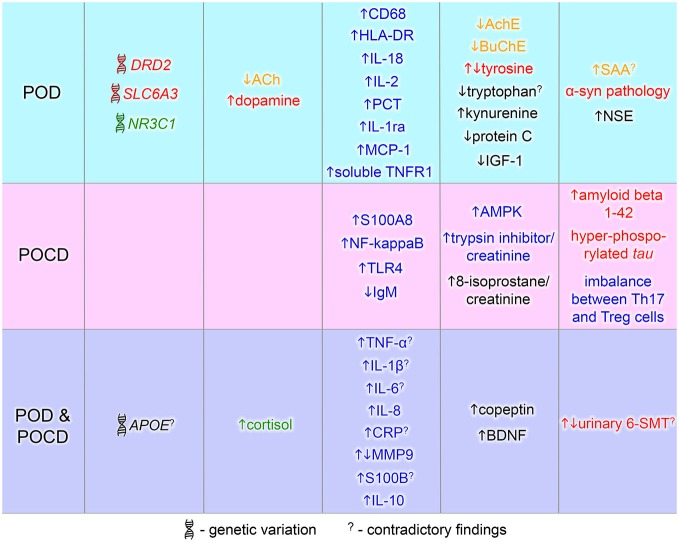
Figure 2.
Biomarkers of postoperative delirium (POD) and postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Biomarkers identified in POD or POCD patients are in blue and pink area respectively. The common POD/POCD biomarkers are presented in the violet area. Font color denotes a marker type: red—dopamine-related marker, green—glucocorticoid-related marker, yellow—cholinergic marker, blue—inflammation-related marker, black—others. 6-SMT, 6-sulfatoxymelatonin; ACh, acetylcholine; AchE, acetylcholinesterase; AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; APOE, apolipoprotein E; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BuChE, butyrylcholinesterase; CD68, cluster of differentiation 68; CRP, C-reactive protein; DRD2, dopamine receptor D2; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen-DR; IGF-1, insulin growth factor-1; IgM, immunoglobulin M; IL, interleukin; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase-9; NF-kappaB, nuclear factor kappa B; NR3C1, nuclear receptor family 3, group C, member 1; NSE, neuron specific enolase; PCT, procalcitonin; S100A8, S100 calcium binding protein A8 (myeloid-related protein-8, calgranulin A); S100B, S100 calcium binding protein B; SAA, serum anticholinergic activity; SLC6A3, solute carrier family 6, member 3; Th17, T helper 17 cells; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor receptor-1; Treg, regulatory T cells; α-syn, alpha-synuclein.