Fig. 5.
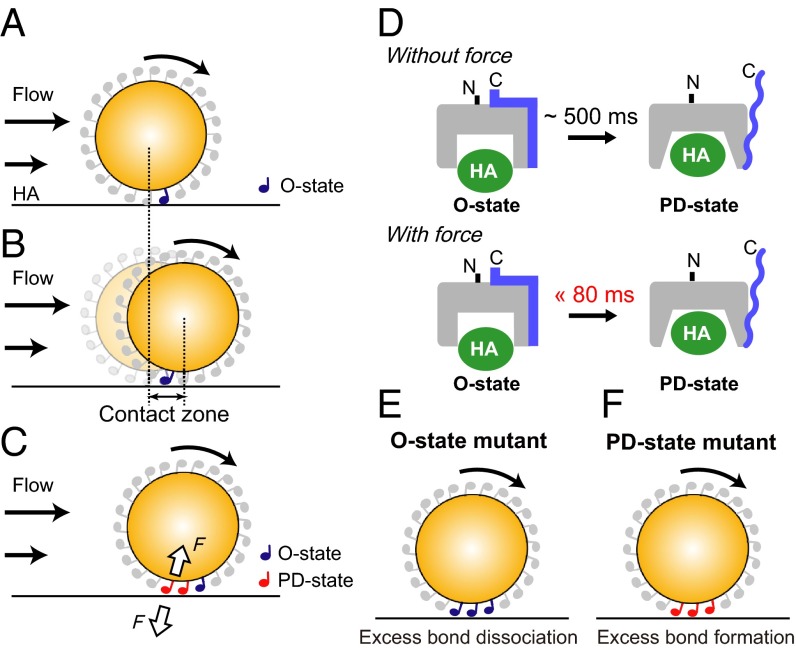
Force-facilitated O-to-PD transition of CD44 HABD in rolling. (A–C) Schematic illustration of the effect of force on the HABD–HA interactions. (A) The initial contact with the HA ligand is mediated by HABD in the O state on the bead. (B) As the bead rolls, the location of the HABD–HA bond reaches the rear end of the bead. The maximum displacement of the bead mediated by a single HABD–HA bond is denoted as the “contact zone.” (C) The tensile force exerted on the HABD–HA bond at the rear end induces the rapid conformational change to the PD state. (D) The O-to-PD transition rates, with or without tensile force. (E and F) Schematic diagram explaining the impaired rolling of the O-state mutant (E) and the PD-state mutant (F).