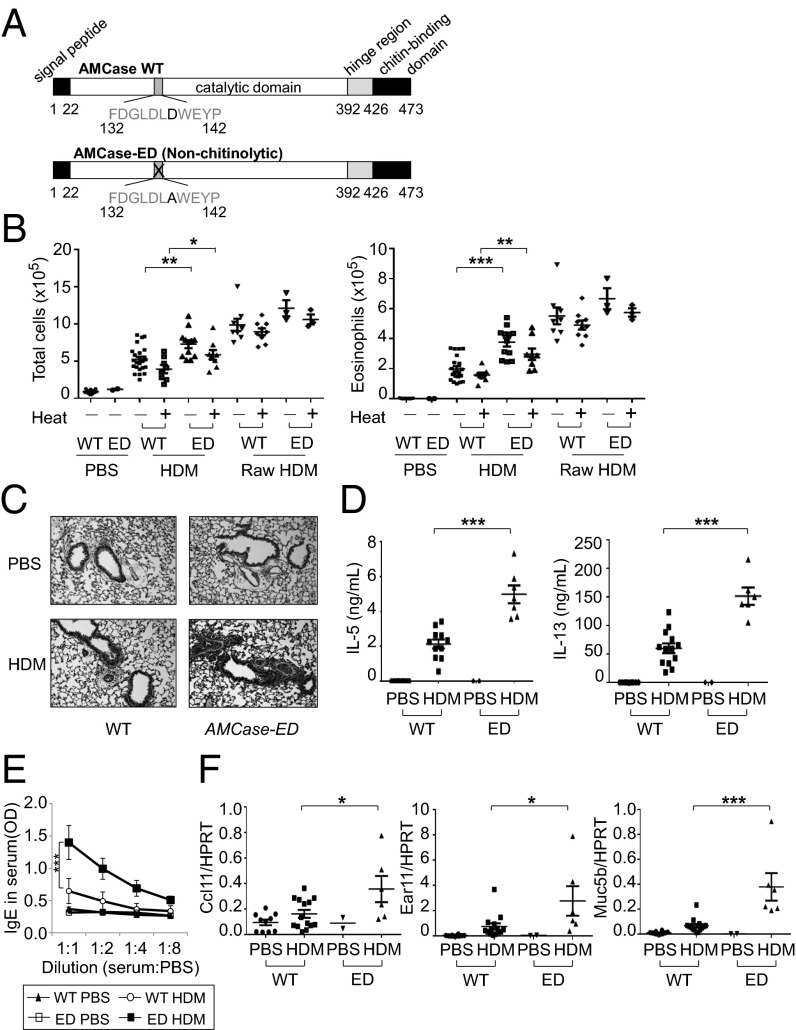
Fig. 1.
Enhanced type 2 immune responses to inhaled HDM in AMCase-ED mice. (A) The schematic domains of AMCase. Aspartic acid is replaced with alanine in active site of catalytic domain of AMCase in AMCase-ED mice. (B) The number of total cells (Left) or eosinophils (Right) in the BAL of WT or AMCase-ED mice after administration of PBS, HDM, or raw HDM with (+) or without (−) pretreatment at 95 °C for 10 min. (C) H&E staining of lung sections of WT or AMCase-ED mice after administration of PBS or HDM (magnification: 20x). (D) The production of IL-5 (Left) and IL-13 (Right). The cells of lung-draining lymph nodes from WT or AMCase-ED mice after administration of PBS or HDM were restimulated in vitro with HDM and mitomycin-C–treated splenocytes for 48 h. Supernatants were collected and analyzed for IL-5 and IL-13 by ELISA. (E) The level of IgE in serum of WT or AMCase-ED mice after administration of PBS or HDM. The serum was diluted with PBS sequentially and analyzed for IgE by ELISA. (F) The expression of ccl11, ear11, and muc5b, normalized to hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase, in the lung of WT or AMCase-ED mice after administration of PBS or HDM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t test. Data were combined from at least four independent experiments. Error bars indicate the SEM.