Figure 5.
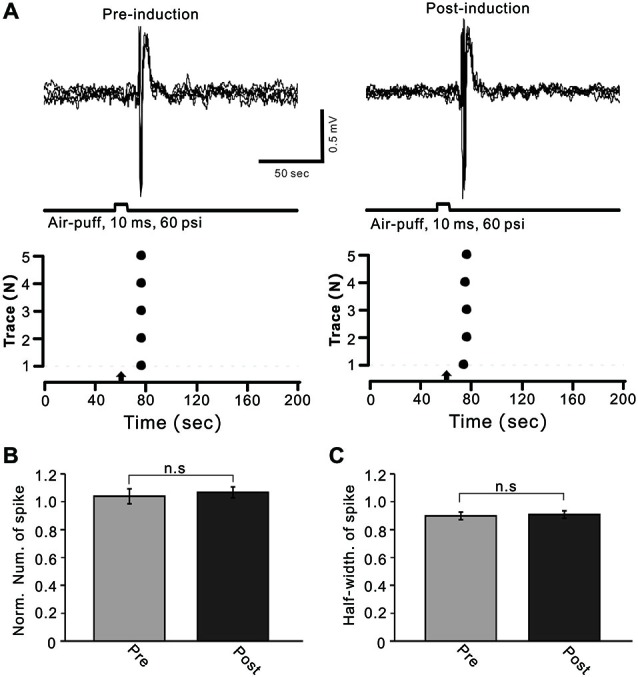
Facial stimulation had a lesser effect on cerebellar MLI activity. (A) Upper, superposition of five representative recording epochs showing air-puff stimulation (10 ms, 60 psi)-evoked spike firing in an MLI before (left) and after (post) delivery of 1 Hz (240 pulses) stimulation. The lower panel shows the master plot of spike events derived from traces of the upper panel. (B) Summary of normalized number of spike events before (Pre, red) and after delivery of 1 Hz stimulation (Post; n = 6). (C) Pooled data showing the normalized half-width of the sensory-evoked spike events before (Pre) and after delivering 1 Hz stimulation (Post; n = 6). Note that air-puff stimulation at 1 Hz did not induce a significant change in the properties of the sensory-evoked spike events on MLIs.
