Fig. 1.
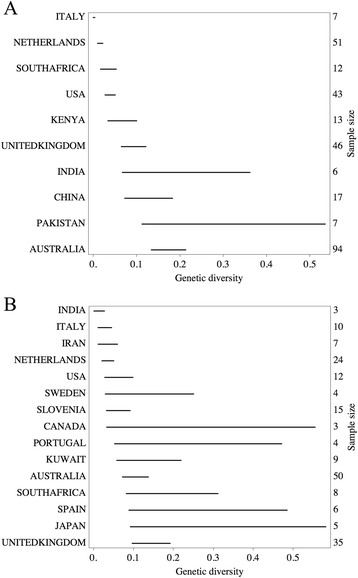
Genetic diversity of two human-infective species of Cryptosporidium. C. hominis (panel a) and C. parvum of human origin (panel b). The horizontal axis represents the genetic diversity of GP60 sequences per nation: a coalescent effective population size multiplied by mutation rate per generation at GP60 locus. The horizontal line aligned to a nation name represents the posterior credible interval around the estimated genetic diversity. The integer next to the right vertical axis is the number of GP60 sequences used in the estimation
