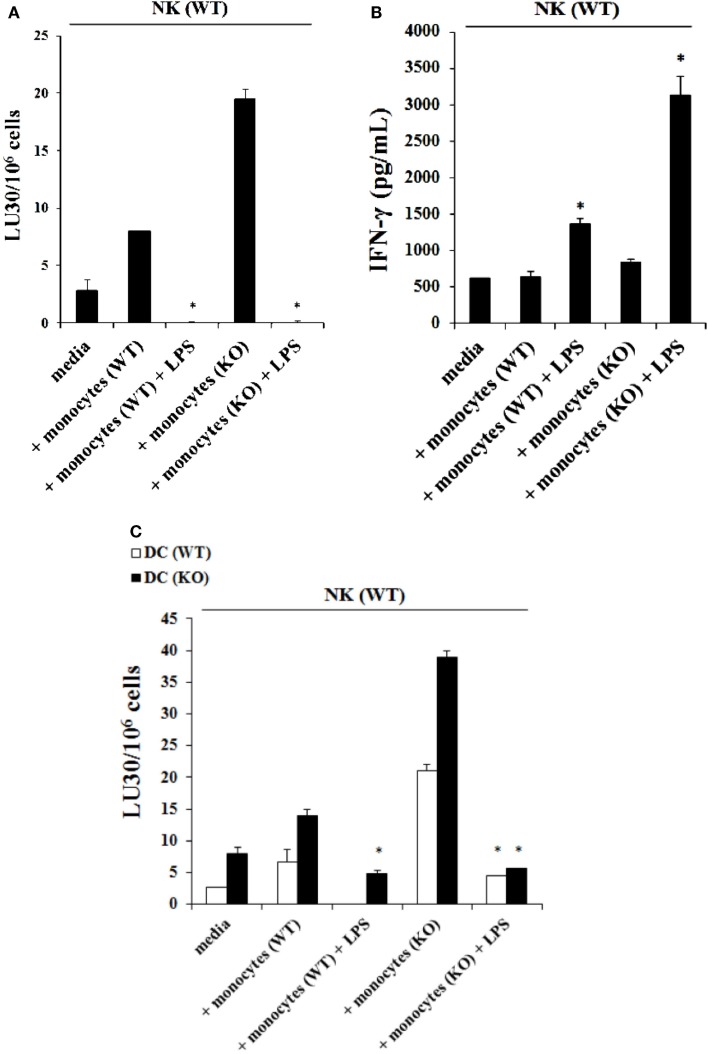
Figure 4.
The addition of LPS to NK cells cultured with monocytes induced split anergy in NK cells which resulted in significant inhibition of NK cell cytotoxicity but increased IFN-γ secretion. IL-2-treated (1 × 104 U/million) NK cells obtained from wild type mice were cultured with monocytes from wild type mice or Cox-2flox/flox;LysMCre/+ mice for 7 days and then treated with or without LPS (20 ng/mL) for an additional day. Afterward, NK cells were used as effector cells in a standard 4 h 51Chromium release assay against YAC-1 cells. The lytic units 30/106 cells were determined using inverse number of NK cells required to lyse 30% of the target cells × 100. *P < 0.05 was obtained for differences in cytotoxicity between untreated and LPS-treated NK cells cultured with monocytes from control littermates or those from Cox-2flox/flox;LysMCre/+ mice (A). NK cells were treated as described in (A) and afterward the supernatant was removed from the co-cultures and the levels of IFN-γ secretion were determined using specific ELISAs. *P < 0.05 was obtained for differences in secretion of IFN-γ between untreated and LPS-treated NK cells cultured with monocytes from control littermates or those from Cox-2flox/flox;LysMCre/+ mice (B). NK cells were prepared as described in (A) and used as effector cells against DCs derived from monocytes from either wild type or Cox-2flox/flox;LysMCre/+ mice in a standard 4 h51Chromium release assay. The lytic units 30/106 cells were determined using inverse number of NK cells required to lyse 30% of the target cells × 100 (C). One of several representative experiments is shown in this figure.