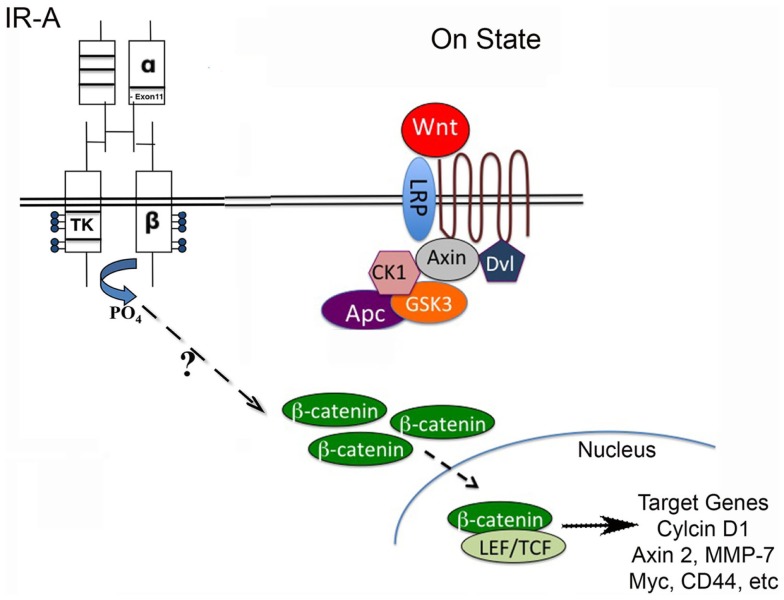
Figure 1.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway regulates stem cell pluripotency and cell fate decisions during development. The Wnt pathway is activated when Wnt ligand binds to a Frizzled receptor, which then is brought into complex with the co-receptor LRP5/6. The activation of the Wnt pathway leads to stabilization of β-catenin through inactivation of the destruction complex (containing Axin, CK1, Gsk3β, and Apc). β-catenin can then translocate to the nucleus and interact with LEF/TCF to regulate Wnt target genes. The stimulation of the insulin receptor isoform A (IR-A) in IGF-1R null (R-/IR-A) fibroblasts by insulin was shown to increase levels of β-catenin through a mechanism that is currently unknown.