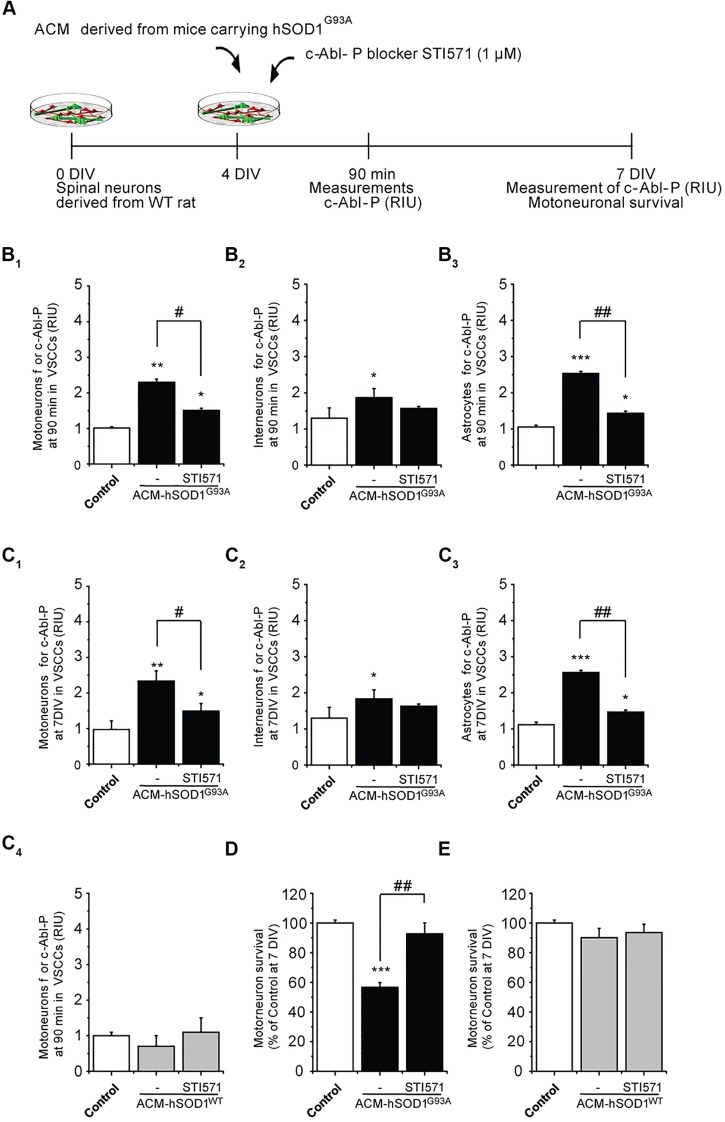
FIGURE 2.
c-Abl kinase inhibitor STI571 prevents motoneuron death induced by ACM-SOD1G93A. (A) Flow diagram of experiment. ACM-SOD1G93A was applied to 4 DIV spinal cord cultures acutely (for 90 min when c-Abl-P peaks; see Figure 1) or chronically (3 days) either alone or in the presence of c-Abl kinase inhibitor STI571 (1 μM). Phosphorylation of c-Abl was measured at 4 and 7 DIV. Cell survival was measured at 7 DIV. (B) Graphs showing fluorescence intensities (RIU) for c-Abl-P at 4 DIV when treated acutely (90 min) with ACM-SOD1G93A alone or ACM-SOD1G93A plus STI571; motoneurons (B1), interneurons (B2) and glial cells (B3) were identified by immunostaining (as in Figure 1). (C1-3) Same as in (B), but c-Abl-P is measured at 7 DIV when treated chronically (3 days) with ACM-SOD1G93A alone or with STI571. (C4) c-Abl-P is measured at 7 DIV when treated chronically (3 days) with ACM-SOD1WT alone or with STI571. (D,E) Graphs showing the relative percentage of motoneurons that survived at 7 DIV, after being treated with STI571 and ACM-SOD1G93A (D) or ACM-SOD1WT (E). Values represent mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments performed in duplicate, analyzed by One-Way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post hoc test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 relative to control conditions. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared to survival with the ALS-causing ACM to at 7 DIV without STI571.