Figure 2.
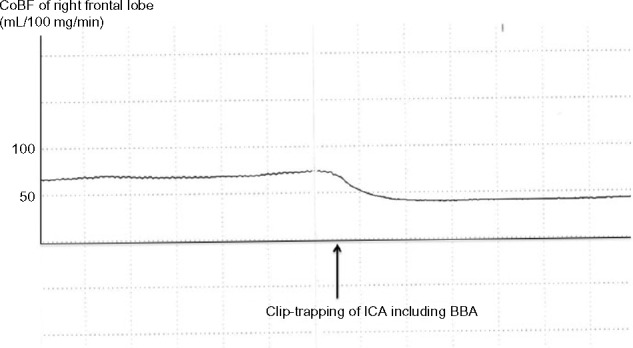
The cortical cerebral blood flow (CoBF) in the frontal lobe decreases immediately after clip-trapping between the area just distal of the origin of the ophthalmic artery and the area just proximal to the origin of the posterior communicating artery, including the ruptured blood blister-like aneurysm (BBA), in the internal carotid artery (ICA). CoBF after clip-trapping decreases by 56% in the right frontal lobe and returns to pre-clamping levels immediately after de-clamping of the ICA.
