Figure 4.
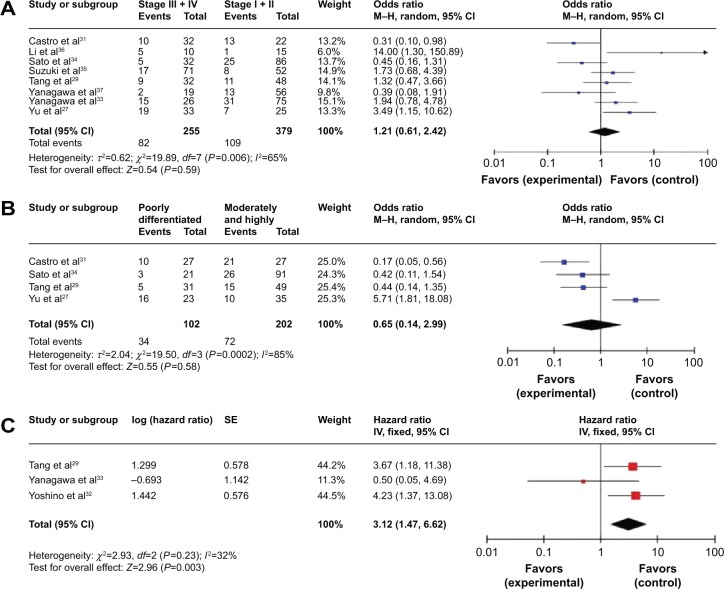
NSCLC patients (n=634) pooled from eight studies to assess whether or not aberrant RUNX3 hypermethylation in NSCLC is associated with a more advanced stage of disease.
Notes: (A) Aberrant RUNX3 hypermethylation was not significantly higher in advanced NSCLC (III and IV) than in early stage NSCLC (I and II; OR 1.21, CI 0.61–2.42, P=0.59). (B) Aberrant RUNX3 hypermethylation was also not significantly higher in poorly differentiated NSCLC than that in moderately and highly differentiated NSCLC (OR 0.65, CI 0.14–2.99, P=0.58). (C) Three included studies investigated relationships between overall survival and RUNX3 hypermethylation. The pooled HR for overall survival showed that RUNX3 hypermethylation was associated with worse survival in NSCLC (HR 3.12, 95% CI 1.47–6.62, P=0.003).
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; OR, odds ratio; M–H, Mantel–Haenszel; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; SE, standard error.