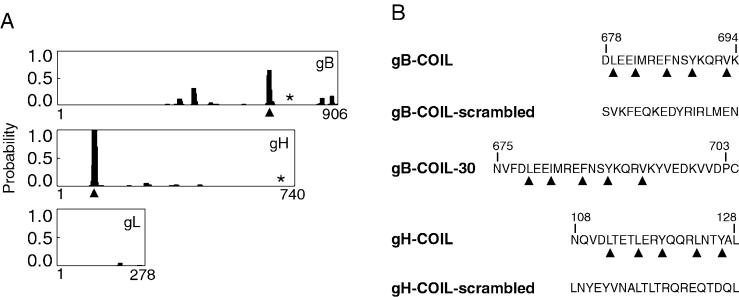
FIG. 1.
Identification of coiled-coil domains in CMV fusogenic glycoproteins. (A) Probability plots for alpha-helical coiled coils were generated using the algorithm by Lupas et al. (21) (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/COILS_form.html). The horizontal axis represents the primary sequence of each protein, and the vertical axis represents the probability for forming alpha-helical coiled coils. Identified heptad repeat regions, predicted to result in coiled-coil structures, are marked with arrowheads. Both gB and gH are predicted to have a single alpha-helical coiled-coil domain with a probability of at least 60%. The membrane-spanning domain of each protein is marked with an asterisk. Note that gL has no membrane-spanning domain but is covalently associated with gH. (B) Peptides including the heptad repeat sequences of the predicted coiled-coil regions of gB and gH were synthesized. Heptad repeat residues are marked with arrowheads, and the amino acids are numbered according to their position within the primary sequence of each protein. Note that peptide gB-COIL-30 has a cysteine residue at its carboxy terminus that is not derived from gB sequence. This cysteine residue was added to facilitate potential chemical modifications to the peptide. Peptides gB-COIL-scrambled and gH-COIL-scrambled contain the same amino acids as gB-COIL and gH-COIL, respectively, but the amino acids have been randomized to eliminate the heptad repeat predicted to give rise to a coiled-coil structure.