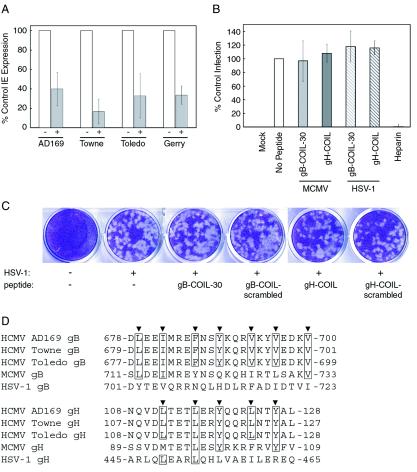
FIG. 6.
Virus specificity of gB and gH peptides. (A) Various strains of CMV were inoculated onto NHDF cells at an MOI of approximately 0.5 PFU/cell in the presence or absence of 500 μM gB-COIL-30 and allowed to bind and penetrate for 40 min at 37°C. Nonpenetrated virus was inactivated, and the cells were incubated 18 to 24 h. Immunofluorescence analysis was performed to detect IE gene products, and the percentage of IE-positive cells was scored for each treatment. Data are reported in triplicate, and error bars represent standard deviations. All strains of CMV tested were vulnerable to the inhibiting activity of 500 μM gB-COIL-30. (B) MCMV-GFP was inoculated onto NIH 3T3 cells at an MOI of approximately 3 PFU/cell in the presence or absence of 500 μM gB-COIL-30 or 500 μM gH-COIL for 60 min at 37°C. Nonpenetrated virus was inactivated, and the cells were incubated for 22 to 24 h at 37°C. GFP expression was detected by fluorescence microscopy, and the percentage of GFP-positive cells was scored for each treatment. Data are reported in duplicate, and error bars represent the range. HSV-1(KOS)gL86 was inoculated onto NHDF cells in the presence or absence of 500 μM gB-COIL-30 or 500 μM gH-COIL for 60 min at 37°C. Nonpenetrated virus was inactivated, and the cells were incubated 6 h at 37°C. β-Galactosidase expression was measured using the colorimetric substrate o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside. Data are reported in triplicate, and error bars represent standard deviations. Neither peptide inhibited MCMV entry into NIH 3T3 cells (light gray bar represents gB-COIL-30; dark gray bar represents gH-COIL) or HSV-1 entry into NHDF cells (light-gray hatched bar represents gB-COIL-30; dark-gray hatched bar represents gH-COIL). In contrast, soluble heparin efficiently blocked entry of HSV-1 into human fibroblast cells (rightmost bar). (C) HSV-1 was inoculated onto NHDF cells in the presence or absence of 500 μM gB-COIL-30, gB-COIL-scrambled, gH-COIL, or gH-COIL-scrambled. Plaques were visualized 3 days postinfection by crystal violet staining. (D) The amino acid sequence of the predicted coiled-coil regions of gB and gH from human CMV strains AD169, Towne, and Toledo, as well as MCMV and HSV-1, are aligned. Heptad repeat residues are indicated by arrowheads above each alignment, and amino acids are numbered according to their position within the primary sequence of each protein. Note that the heptad repeat sequences are identical among the three human CMV strains for both gB and gH, while the MCMV and HSV-1 strains show both conservative and nonconservative substitutions at the heptad repeat sequences of gB and gH compared to the human CMV strains. The conservation of the heptad repeat sequences, or lack thereof, positively correlates with the ability of the human CMV strain AD169-derived gB and gH peptides to inhibit virus entry.