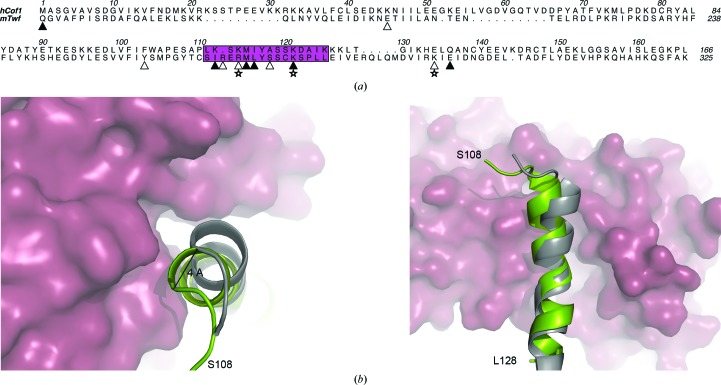
Figure 5.
(a) Structure-based sequence alignment of hCof1 and the C-terminal part of twinfilin (Twf-C). The actin-binding helix (α5 in hCof1) is shown in magenta. Residues that are predicted to form hydrogen bonds between actin and Twf-C or hCof1 are marked with filled triangles and residues that are only predicted to form hydrogen bonds between actin and Twf-C are marked with open triangles. Salt bridges between actin and Twf-C are labelled with open stars. (b) Top and side view of a cartoon representation of the actin-binding helix from Twf-C (grey) and hCof1 (green). The hCof1 helix clashes with actin (raspberry surface). The 4 Å shift of the helix to accommodate binding to actin is highlighted.