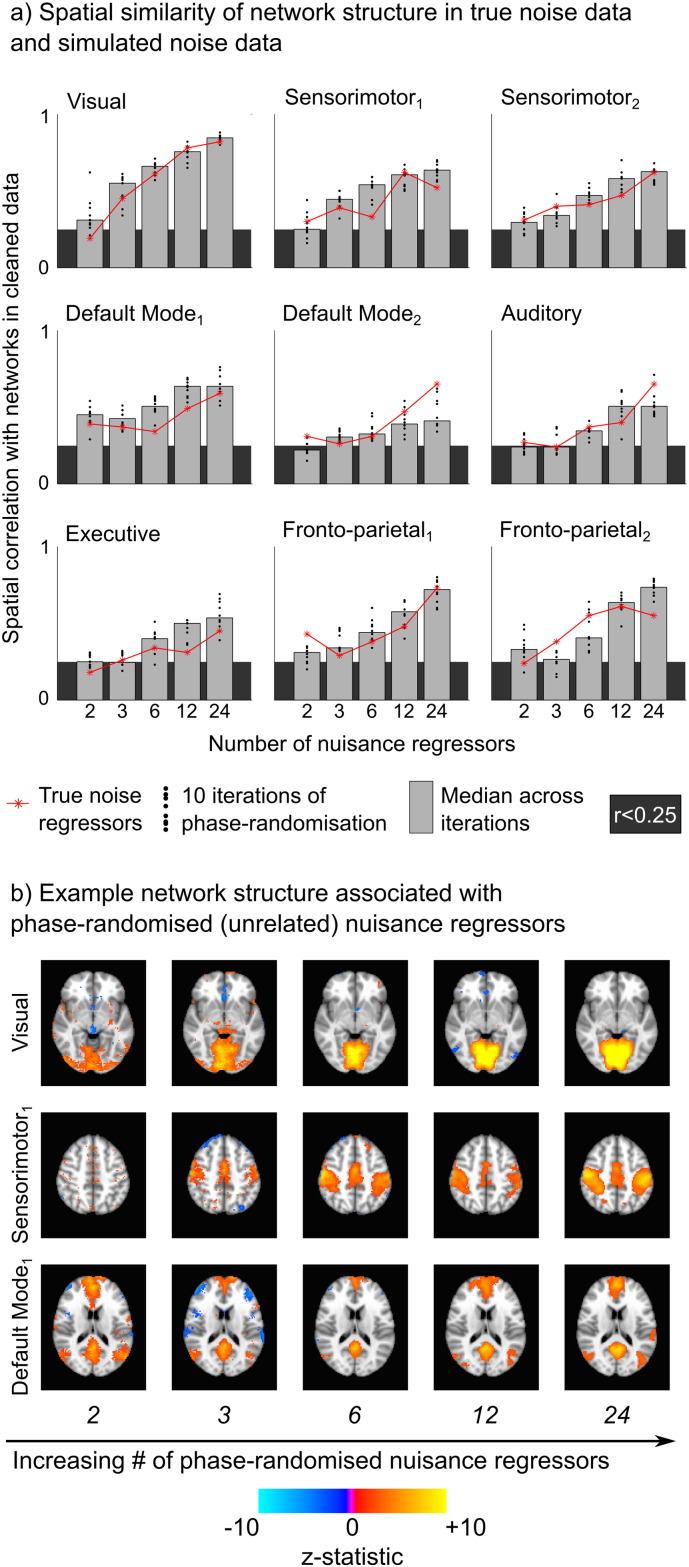
Fig. 3.
a) Spatial correlation comparing the networks in the cleaned data to those in true noise data (red lines) or simulated noise datasets (black points representing 10 iterations, median value indicated by grey bars). Dark grey shading indicates non-significant similarity (r < 0.25). Both true and simulated noise contain these two networks with high fidelity in the case of 12 or 24 nuisance regressors, suggesting that the network structure in the noise variance is not inherently linked to true noise and can be achieved via unrelated (orthogonalised) nuisance regressors. b) The maps demonstrating the median spatial correlation value across the 10 iterations of simulated noise datasets is provided for 3 networks (Visual, Sensorimotor1 and Default Mode1).