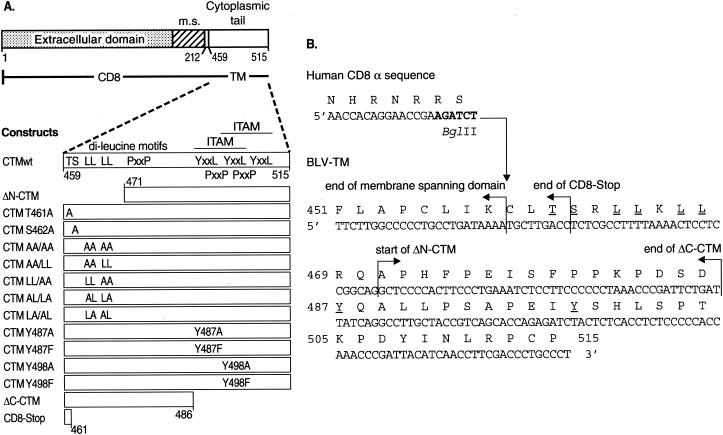
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of CD8-CTM chimeric proteins. The top diagram represents the entire CD8-CTM fusion construct. The extracellular and membrane spanning (m.s.) domains plus four to seven cytoplasmic amino acids of CD8-α (aa 1 to 212) precede the BLV CTM (aa 459 to 515 of the BLV Env protein precursor). The expanded diagram of the wt CTM of T-15 BLV shows the locations of T461, S462, two dileucine motifs, three PXXP motifs, and the three YXXL motifs that form two overlapping ITAMs. Mutations are shown in their approximate locations. ΔN-CTM lacks 12 N-terminal amino acids of the BLV CTM, whereas ΔC-CTM lacks 29 C-terminal residues. CD8-Stop contains only the first three amino acids of the BLV CTM. (B) DNA and amino acid sequences of chimeric CD8-CTM constructs. The end of the CD8-α sequence encodes membrane-spanning and cytoplasmic amino acids just upstream of the junction with the BLV CTM; the BglII restriction site used to fuse the sequences is in bold type. The end of the predicted membrane-spanning domain (48, 52) of the BLV CTM is demarcated; the predicted cytoplasmic domain begins at C459, which is the first BLV-encoded amino acid in all CD8-CTM chimeras except ΔN-CTM. Arrows indicate the start of BLV-specific sequences of the ΔN-CTM chimera as well as the ends of the CD8-Stop and ΔC-CTM chimeras. Individual amino acids that were replaced are underlined.