Figure 1. Characterization and toxicity of curc-np.
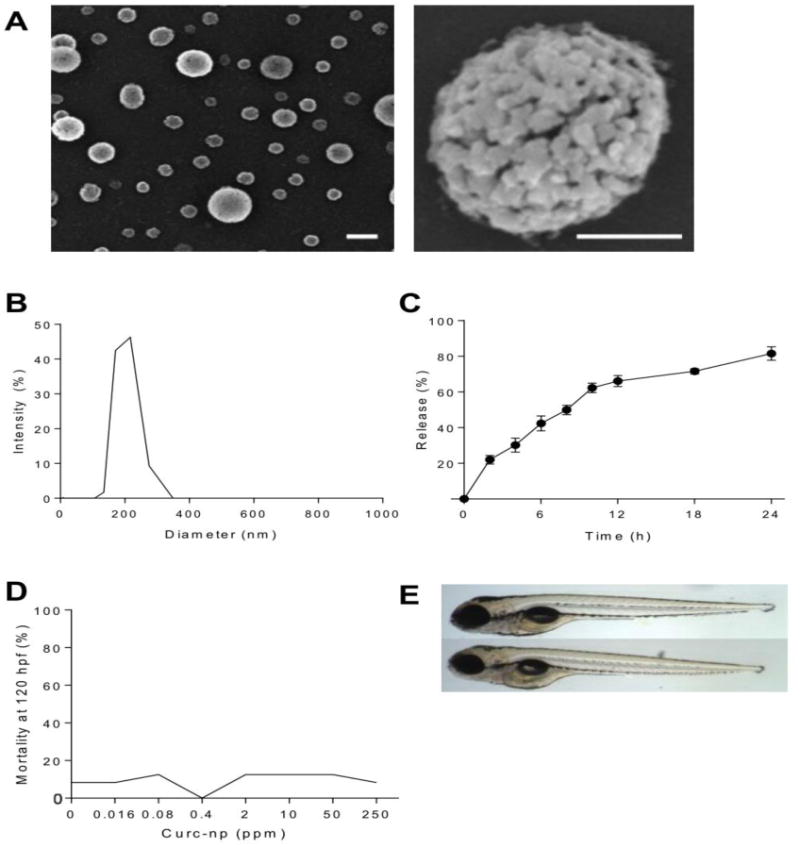
(A) Scanning electron microscopy revealed distinct spherical nanoparticles (left bar=200 nm, right bar=100 nm). (B) Monomodal size distribution quantified by dynamic light scattering indicated a narrow size range with average diameter 222 ± 14 nm. (C) Release occurred in controlled and sustained fashion, reaching 81.5% after 24 hours. (D) Percent mortality at 120 hours post-fertilization (hpf) as a function of exposure concentration. Mortality was not significant for embryos exposed to curc-np compared to fish water control. (E) Representative images of zebrafish embryos at 120 hpf: control (top) and exposed to curc-np (bottom). No significant differences were observed in larval morphology or behavioral endpoints (p>0.05 for each endpoint evaluated, Fisher's Exact test). Error bars denote SEM.
