Figure 4. Curc-np decrease bacterial burden of full-thickness burns.
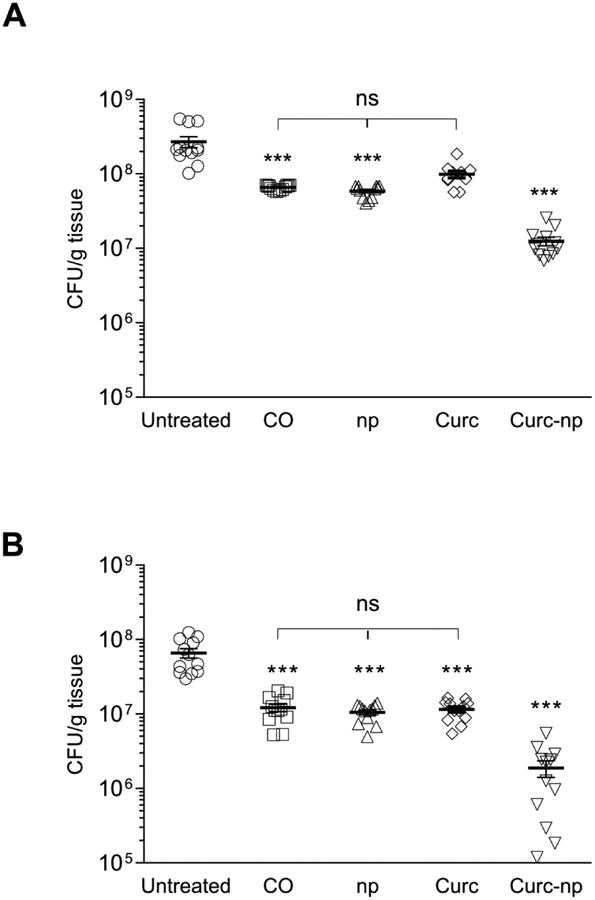
Wound bacterial burden (CFU; colony forming unit) in mice infected intradermally with 5 × 108 MRSA cells was determined by amount of CFU growth (n=10 wounds per group). On day 3 (A) and day 7 (B) after infection, bacterial burden of curc-np-treated wounds was significantly lower than untreated, coconut oil (CO), control np (np), and curcumin (curc)-treated wounds. Statistical analysis conducted using 1-way ANOVA. Error bars denote SEM. *** p≤0.001, ns p>0.05.
