Figure 5. Curc-np accelerate wound healing in a murine burn model.
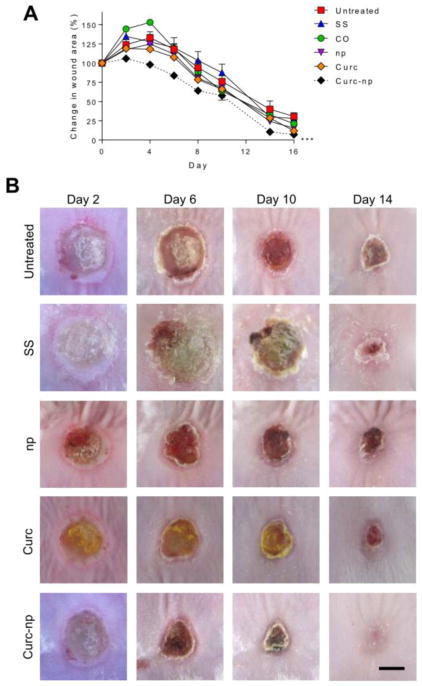
(A) Wound size analysis (relative area versus initial area) revealed statistically significant acceleration of wound healing in mice treated with curc-np compared to untreated, silver sulfadiazine (SS), coconut oil control (CO), control np (np), and curcumin (curc). Time points are averages of 10 measurements. Statistical analysis conducted using 2-way ANOVA. Error bars denote SEM. *** p≤0.0001. (B) Representative images of wound healing from days 2-14. Topical administration of curc-np decreased eschar size and qualitatively accelerated healing compared to all other groups. CO (vehicle) control did not differ significantly from untreated control (data not shown). Scale bar=5 mm.
