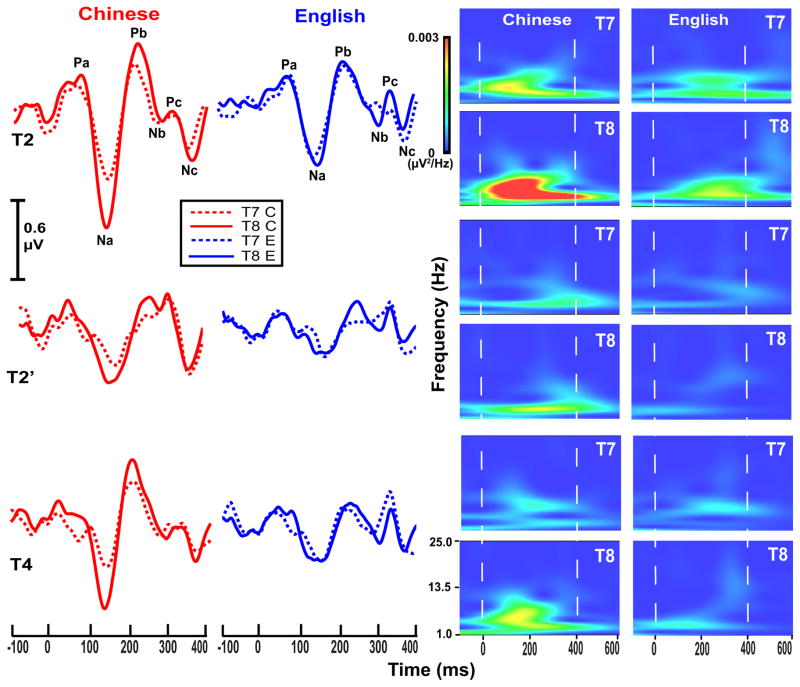
Figure 4.
Grand average waveforms (left) and their corresponding spectra (right) of the CPR components for the two language groups (Chinese, English) recorded at electrode sites T7 (dashed) and T8 (solid) for each of the three stimuli (T2, T2′, T4). CPR waveforms appear to show a right-sided preference (T8 > T7) for the Chinese group especially in response to pitch stimuli with a late acceleration peak representative of native lexical tones (T2, T4). The robust rightward preference for T2 and T4 is clearly evident in the spectrotemporal plots. For either group, no hemisphere effects are observed in response to T2′, a pitch pattern that does not occur in any of the world’s tonal inventories. The zero on the x-axis denotes the time of onset of the pitch-eliciting segment of the three stimuli. Na–Pb and Pb–Nb time windows are demarcated by two vertical, white dashed lines.