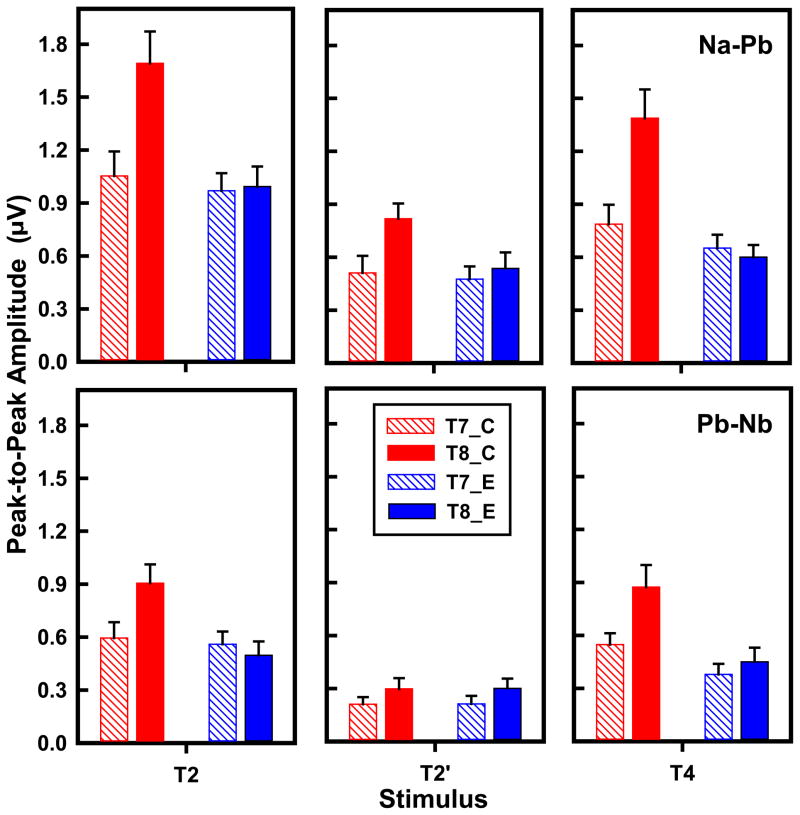
Figure 5.
Mean peak-to-peak amplitude of CPR components (Na-Pb, top row; Pb-Nb, bottom row) extracted from T7/T8 in the temporal lobe as a function of language group (Chinese, red; English, blue), stimulus (T2, T2′, T4), and hemisphere (left, diagonal; right, solid). Na-Pb amplitude shows a hemispheric asymmetry favoring the RH (T8 > T7) in response to T2 and T4 in the Chinese group only. These same two pitch stimuli also elicit a language group difference (C > E) in the RH only. Both T2 and T4 are larger than T2′ only in the RH for the Chinese group. Pb-Nb amplitude similarly reveals a rightward asymmetry in the Chinese group exclusively as well as Chinese superiority relative to English in the RH. Error bars = ±1 SE. C, Chinese; E, English.