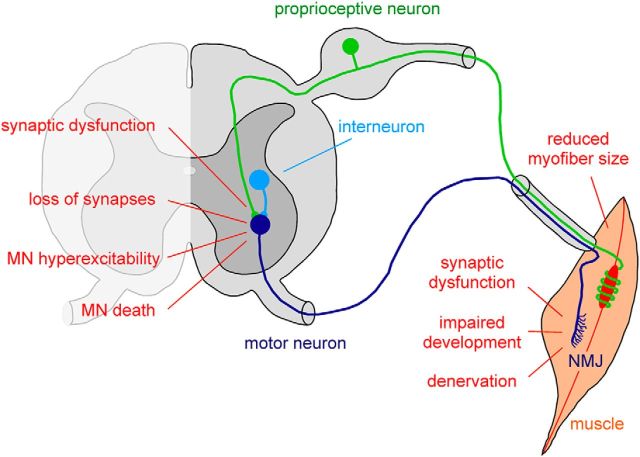
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the key morphological and functional abnormalities induced by SMN deficiency in the motor system of SMA mouse models. Multiple aspects of the motor system are disrupted in SMA. For simplicity, only the excitatory premotor neurons of the motor circuit affected by the disease are depicted. Motor neurons (dark blue) in the ventral horn of the spinal cord receive excitatory synaptic inputs from proprioceptive neurons residing in the dorsal root ganglion (green) and local interneurons (light blue). Upon sufficient excitatory drive to generate action potentials, motor neurons innervating skeletal muscle induce muscle contraction through cholinergic neurotransmission at the NMJ. The specific deficits within the SMA motor system are indicated and are described in detail in the text.