Figure 1.
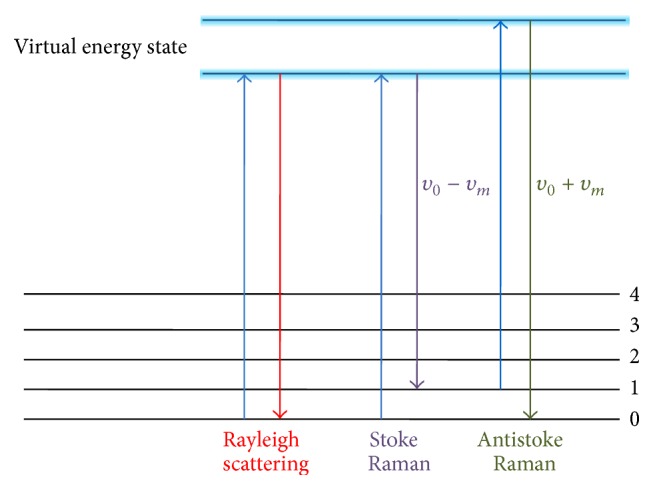
Three types of scattering: Rayleigh, Stoke, and Antistoke. Rayleigh scattering is a interaction that the excited molecule returns back to the same basic vibrational state and emits light with the same frequency υ 0 as an excitation source. Raman scattering occurs when a photon with frequency υ 0 is excited by Raman-active molecule. Stoke frequency is generated by the part of the photon energy is transferred with frequency υ m and the resulting frequency of scattered light is diminished to υ 0 − υ m. Antistoke frequency is released when a photon with frequency υ 0 is excited by a Raman active molecule with already excited vibrational state. The energy level goes up to υ 0 + υ m. Finally released frequency of scattered light from high virtual energy state to the ground state coincides with υ 0 + υ m.
