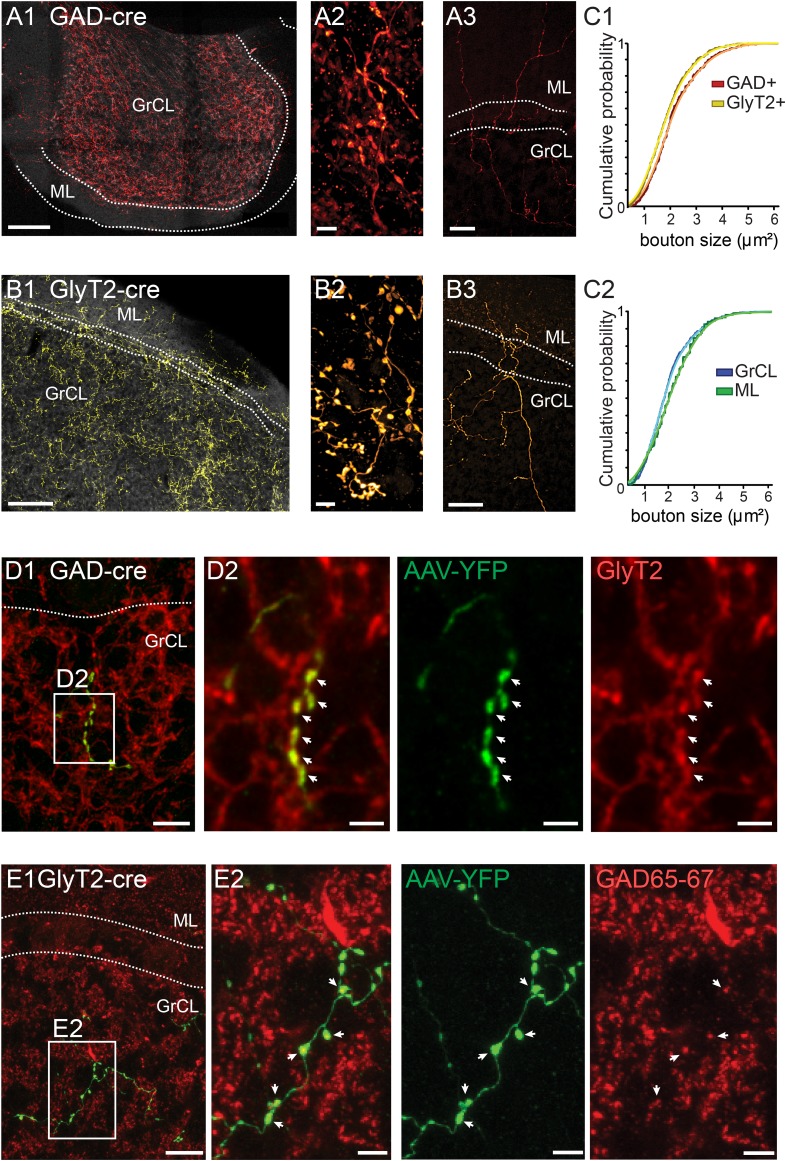
Figure 2. iNC axons are found in cerebellar granule cell and molecular layers and contain GAD65-67 and GlyT2.
(A–B) Confocal composite images of sections through the flocculus in GAD-cre (A1) and posterior vermis in GlyT2-cre (B1) mice, showing dense iNC axons in the GrCl as well as sparse axons in the ML (arrows). 40× composite tiles. Large axonal swellings from both GABAergic (A2) and glycinergic (B2) axons are found in the GrCL. Both GABAergic (A3) and glycinergic (B3) iNC axons occasionally rise into the lower ML. (C) Comparison of iNC axonal bouton sizes between the GABAergic and glycinergic axons (C1) and between the boutons in the GrCL and ML (C2) shows nearly identical distributions. (D) Merged confocal image (Z-projection thickness: 12.2 μm) showing iNC axons in GAD-cre mice injected with AAV-flox-EYFP (green) are co-stained for GlyT2 (red) (D1). Higher magnification of axonal swellings (arrows) co-stained for EYFP and GlyT2 (D2). (E) iNC boutons (green) transfected with AAV-flox-EYFP in GlyT2-cre mice are stained for GAD65-67 (red, E1, Z-projection thickness: 8.2 µm). (E2) Higher magnification of iNC axon (arrows) co-stained for EYFP and GAD65-77 (Z-projection thickness: 2.4 µm). Abbreviations: GrCL, granule cell layer; ML, molecular layer; PNL, Purkinje neuron layer; WM, white matter; n.s., non-significant. Scale bars: A1 and B1: 100 μm; A2 and B2: 5 μm; A3 and B3: 50 μm. D1: 20 μm. D2–4: 5 μm. E1a-e: 10 μm; E2a-e: 2 μm.