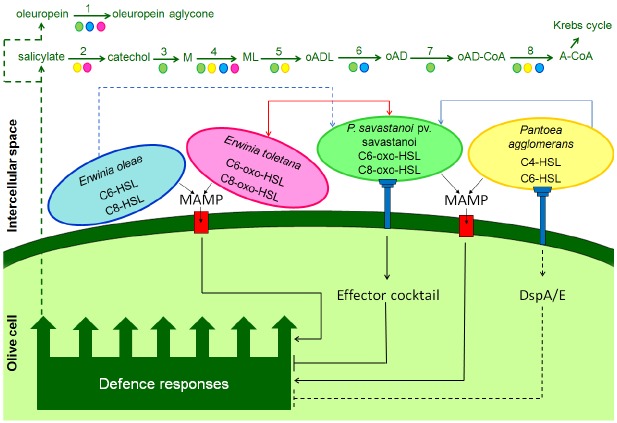
FIGURE 1.
Model representing the interactions between olive cells, Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi (Psv, green bacterial cell) and the endophytes, Pantoea agglomerans (Pa, yellow), Erwinia toletana (Et, pink), and Erwinia oleae (Eo, blue). In the intercellular space of the olive tissues, Psv and Et produce and perceive the quorum sensing signals C6-3-oxo-HSL and C6-3-oxo-HSL (symmetrical sharing, red line). Pa (blue line), and probably Eo (dashed blue line), establish an asymmetrical sharing with Psv. In fact, Pa produce the quorum sensing signals C4-HSL and C6-HSL, which one or both are perceived by Psv; Eo produces C6-HSL and C8-HSL. Microbial associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) are produced by Psv and the other endophytes (e.g., flagellin); they are recognized by specific plant receptors (red box) and defense responses are activated in the host plant (MAMP-triggered immunity, MTI). Among the defense responses, accumulations of salicylic acid (SA) and other phenolic compounds (e.g., oleuropein) can occur in the intercellular space. By contrast, the following enzymes present in the genomes of Psv, Pa, Et, and Eo could collaborate in demolishing SA and oleuropein: (1) β-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21); (2) salicylate hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.1); (3) catechol 1,2-dioxygenase 1 (EC 1.13.11.1); (4) muconate cycloisomerase (EC 5.5.1.1); (5) muconolactone isomerase (EC 5.3.3.4); (6) β-ketoadipate enol-lactone hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.24); (7) 3-oxoadipate CoA-transferase subunit A (EC 2.8.3.6); and (8) acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.16). In addition, through the type III secretion system (pilus Hrp), Psv injects a cocktail of effectors inside the olive cells, many of which are involved in suppressing plant defense responses. Also Pa, which has a complete hrc/hrp gene cluster, could inject the defense-suppressive effector DspA/E. M = cis, cis-muconate; ML, (+)-muconolactone; oADL, 3-oxoadipate-enol-lactone; oAD, 3-oxoadipate; oAD-CoA, 3-oxoadipyl-CoA; A-CoA, acetyl-CoA.