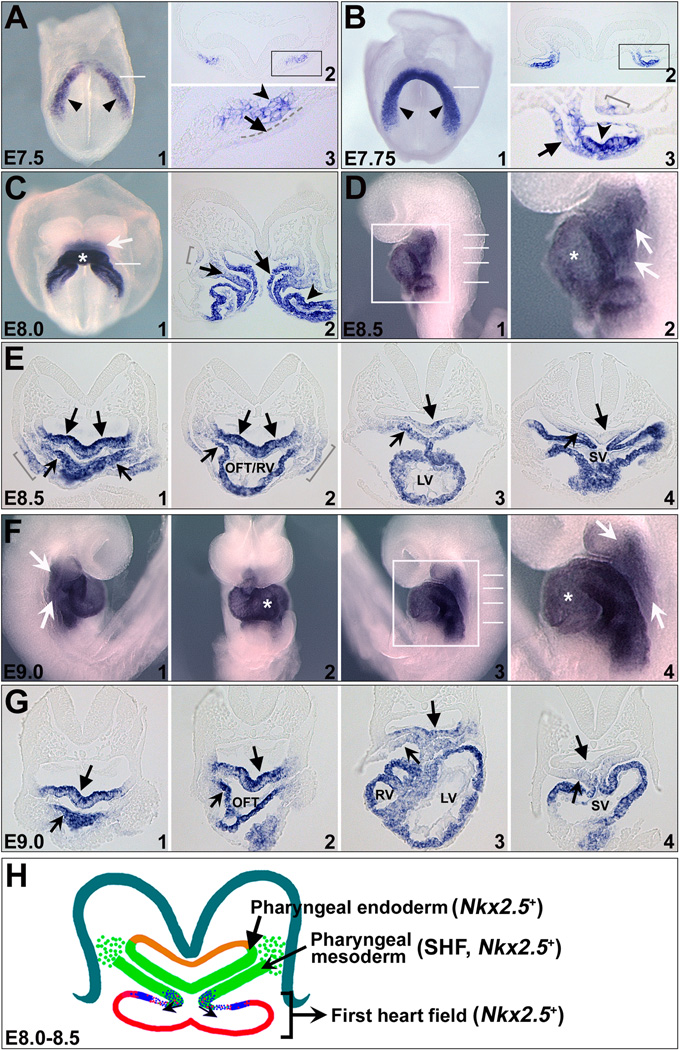
Figure 1. Expression of Nkx2.5 in the FHF, SHF and pharyngeal endoderm during early mouse embryogenesis.
(A-G) Whole-mount RNA in situ hybridization of Nkx2.5 expression in E7.5-E9.0 mouse embryos. A1/B1/C1 are frontal views and D1 is a left lateral view of mouse embryos at corresponding stages. F1/2/3 are right lateral, frontal and left lateral views of E9.0 embryo. A2/B2/C2/E1-5/G1-5 are transverse sections of embryos with approximate positions shown by white lines in A1/B1/C1/D1/F3. A3/B3/D2/F4 are high magnification images of A2/B2/D1/F3 in the square areas, respectively. Unnotched arrowheads in A1/B1 indicate cardiac crescent. Unnotched arrows in A3/B3 indicate splanchnic endoderm. Notched arrowheads in A3/B3 indicate cardiogenic mesoderm. Arrows in C/D/F indicate Nkx2.5 expression in the pharyngeal regions, including pharyngeal mesoderm (notched arrows in C2/E/G) and endoderm (unnotched arrows in C2/E/G) and ectoderm (brackets in B3,C2,E1/2). Asterisks in C/D/F indicate FHF cells. (H) Schematic of Nkx2.5 expression in E8.0-E8.5 mouse embryos with transverse section in the pharyngeal region. Nkx2.5 is expressed in both the FHF-derived linear heart tube (red) and pharyngeal mesoderm SHF (green, notched arrow), as well as pharyngeal endoderm (green, unnotched arrow). OFT, outflow tract; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle.