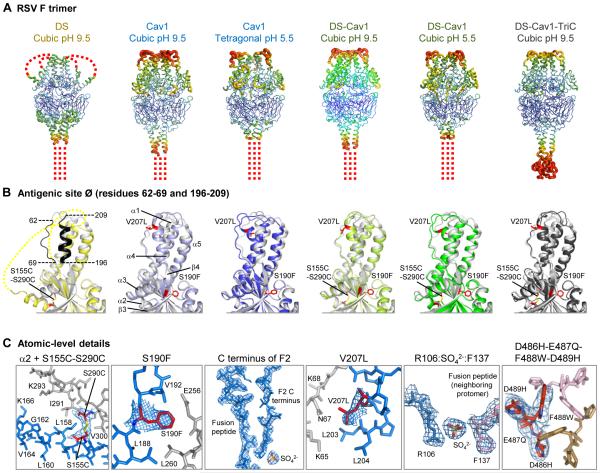
Fig. 2. Crystal structures of RSV F trimers, engineered to preserve antigenic site Ø.
(A-C) Six structures for RSV F variants are shown, labeled by stabilizing mutation (DS, Cav1, DS-Cav1, and DS-Cav1-TriC) and the crystal lattice (cubic or tetragonal). (A) RSV F trimers are displayed in Ca-worm representation, colored according to atomic mobility factor, with regions of higher flexibility in warmer colors (red) and regions of lower flexibility in cooler colors (blue). Missing regions are shown as dotted lines. These occur at the C-terminal membrane-proximal region, where the foldon motif is not seen, except in the DS-Cav1-TriC structure (far right). In the DS structure, two loops in the head region are also disordered. (B) Antigenic site Ø of a RSV F protomer is displayed in ribbon diagram, with the structure of D25-bound RSV F in gray and different variants colored yellow (DS), light and dark blue (Cav1), light and dark green (DS-Cav1), and black (DS-Cav1-TriC). Residues corresponding to antigenic site Ø are highlighted in black on the image at far left, and secondary structural elements are shown on the second image from left. Stabilizing mutations are labeled and shown in stick representation (colored red). Perpendicular view presented in figure S8. (C) Atomic-level details are shown in stick representation, colored the same as in Fig. 2, with regions of RSV F that change conformation between prefusion and postfusion conformation in red and blue, and those that remain constant in gray. Stabilizing carbon atoms for stabilizing mutations are highlighted in red. In Cav1 (pH5.5) and in DS-Cav1 (pH5.5) novel features were observed involving the interaction of the C-terminus of the F2 peptide with a sulfate ion and the fusion peptide. In the DS-Cav1-TriC structure, the D486H-E487Q-F488W-D489H mutations interact with the two neighboring protomers (colored tan and pink) around the trimer axis.