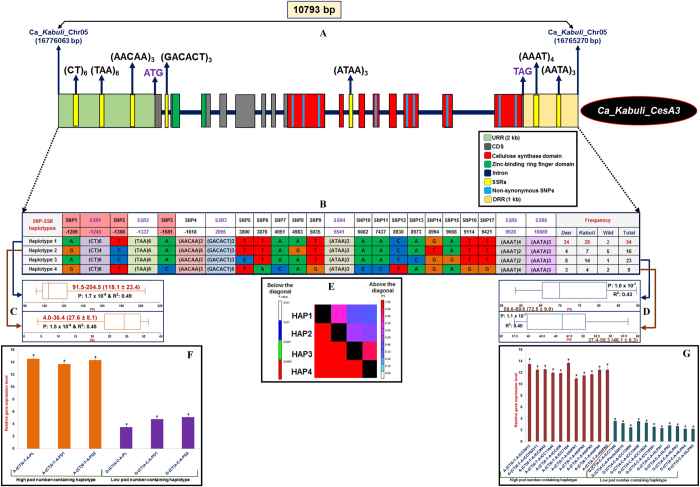
Figure 9. The gene haplotype-specific LD/association mapping and expression profiling in a strong PN- and SN trait-associated Ca_Kabuli_CesA3 gene, validating its potential for regulating pod/seed number in chickpea.
The genotyping of 91 SNPs and 7 SSRs in different coding and non-coding sequence component of cellulose synthase gene (A) among 102 accessions (92 association panel and 10 wild accessions) constituted four haplotypes (B). The two-specific haplotypes, haplotype 1: [A-(CT)6-T-A] and haplotype 2: [G-(CT)4-C-A], which were determined by three SNPs (−1209, −1308 and −1581 bp) and one SSR (−1245 bp) in the URR of gene showed strong association potential for high and low pod number differentiation, respectively (C). The four haplotype marker-based genotyping information produced greater LD estimates (r2 > 0.70 with P < 1.4 × 10−4) covering the entire 10793 bp sequenced region of the gene (D). The differential up-regulated expression of one high pod number-regulating superior haplotype in the URR of a Ca_Kabuli_CesA3 gene was evident in mature pollen and two pod developmental stages of high pod number-containing accessions (E), homozygous mapping individuals and parental accession (ICC 6013) compared with that of low pod number accessions. HHPN: homozygous high pod number and HLPN: homozygous low pod number.