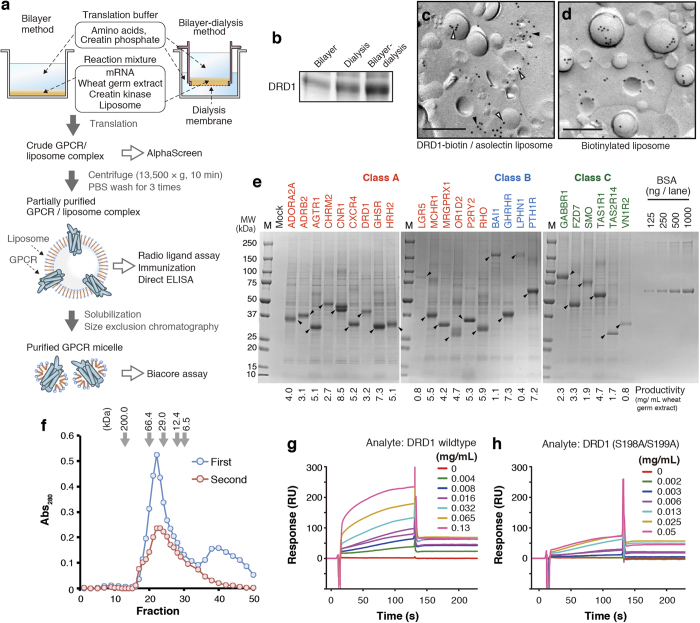
Figure 1. Production and purification of GPCRs using wheat cell-free synthesis system.
(a) A schematic representation. Wheat cell-free synthesis of GPCR was conducted by bilayer method15 or bilayer-dialysis method. GPCR/liposome complex or solubilized GPCR micelle was prepared depending on the purposes. (b) Comparison of productivity between the synthesis methods. DRD1 was synthesized with each method. The ratio of wheat germ extract: liposome: mRNA was shared. DRD1 liposome was partially purified by centrifugation, and purified liposome containing 0.8 μg lipid was subjected to SDS-PAGE. CBB staining image is shown. (c) Immunogold labeling of DRD1-biotin/liposome complex. Bar, 0.2 μm. Blank arrowheads indicate DRD1-biotin located on liposome, and filled arrowheads present ones on lipid structures in close association with liposomes. (d) Immunogold labeling of biotinylated liposome. Bar, 0.2 μm. (e) SDS-PAGE image of cell-free synthesized GPCRs. Twenty five GPCRs were synthesized by bilayer-dialysis method with 100 μL reaction mixture containing 25 μL of wheat germ extract. GPCR/liposome complexes were partially purified by centrifugation and PBS, and then resuspended into 100 μL of PBS. Two μL liposome suspension was applied to SDS-PAGE and CBB staining. Arrowheads indicate target GPCRs. BSA standards were also applied. (f) SEC elution profile of solubilized DRD1. Partially purified DRD1 liposome was solubilized by DDM-containing buffer and subjected to SEC (first run, blue). DRD1 peak fractions in first run (fraction 18–25) were collected, concentrated by ultrafiltration, and applied to SEC (second run, red). (g, h) Biacore analysis of DRD1. Dopamine and histamine were immobilized on the measuring cell and reference cell of a sensor chip, respectively. DRD1 wild-type (c) or S198A/S199A mutant (d) micelle was injected as analyte.