Figure 2.
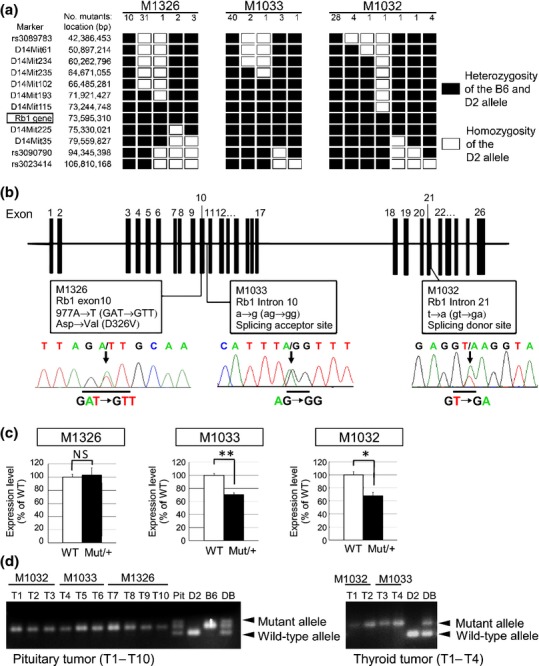
Identification of retinoblastoma gene (Rb1) as causal gene in the three mutant lines generated by N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea mutagenesis. (a) Fine mapping study on chromosome 14 using SSCP and single nucleotide polymorphism markers. Haplotype analysis of D2-backcrossed N2-N3 progeny was performed. (b) The mutations found in exon 10 (M1326), intron 10 (M1033) and intron 21 (M1032) are shown in the exon-intron structure of mouse Rb1. Arrows indicate the mutations in the sequence chromatograph. (c) qPCR of Rb1 mRNA levels in the three Rb1 hetero mutants (Mut/+) or wild-type littermates (WT; n = 3 per genotype). Statistical analysis: unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. NS, not significant. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. Error bar, SD. (d) LOH at the Rb1 locus was confirmed in pituitary tumors (left; T1–T10) and thyroid tumors (right; T1–T4) derived from Rb1 mutants. Pit, pituitary DNA from a WT mouse. D2, B6 and DB: genomic DNA derived from D2, B6 and DBF1 mice, respectively.
