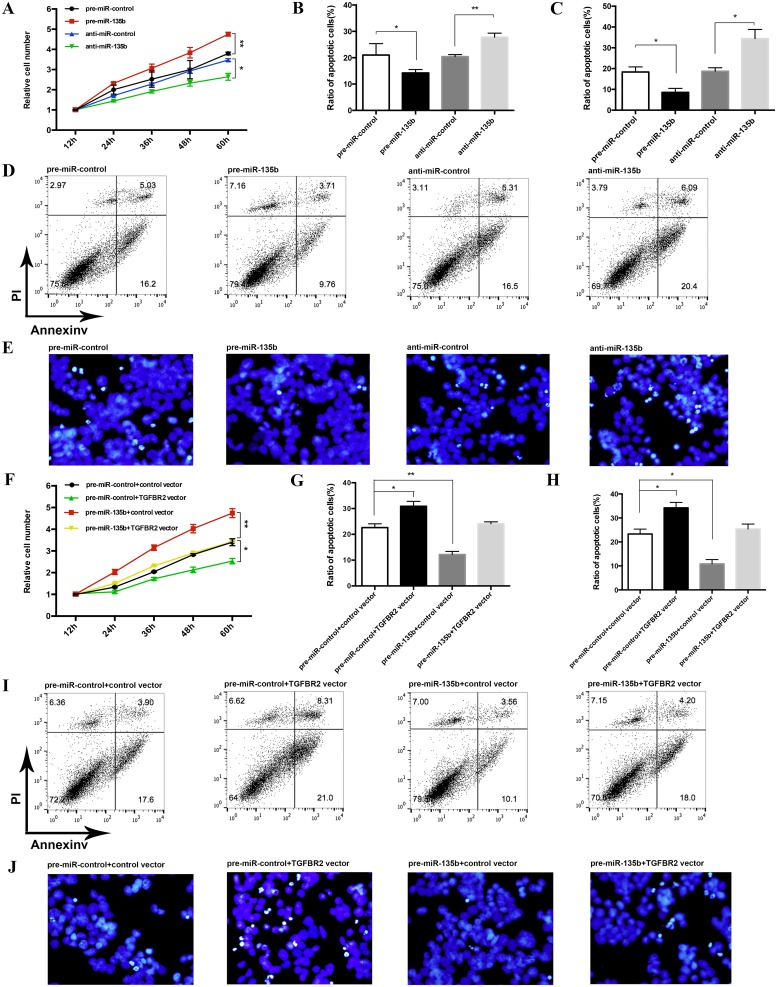
Fig 5. The effect of miR-135b on the proliferation and apoptosis of CRC cells.
(A) CCK-8 cell viability assays were performed 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 h after the transfection of HT-29 cells with pre-miR-control, pre-miR-135b, anti-miR-control or anti-miR-135b. (B-E) Apoptosis assays were performed 24 h after the transfection of HT-29 cells with pre-miR-control, pre-miR-135b, anti-miR-control or anti-miR-135b. B: representative percentage of apoptotic HT-29 cells using flow cytometric analysis; C: representative percentage of apoptotic HT-29 cells using DAPI staining; D: representative image using flow cytometric analysis; C: representative image of apoptotic HT-29 cells using DAPI staining. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. (F) CCK-8 cell viability assays were performed 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60 h after the transfection of HT-29 cells with the scrambled control miRNA and the control vector, the scrambled control miRNA and the TGFBR2 vector, pre-miR-135b and the control vector, or pre-miR-135b and the TGFBR2 vector. (G-J) Apoptosis assays were performed 24 h after the transfection of HT-29 cells with the scrambled control miRNA and the control vector, the scrambled control miRNA and the TGFBR2 vector, pre-miR-135b and the control vector, or pre-miR-135b and the TGFBR2 vector. G: representative percentage of apoptotic HT-29 cells using flow cytometric analysis; H: representative percentage of apoptotic HT-29 cells using DAPI staining; I: representative image using flow cytometric analysis; J: representative image of apoptotic HT-29 cells using DAPI staining. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01.