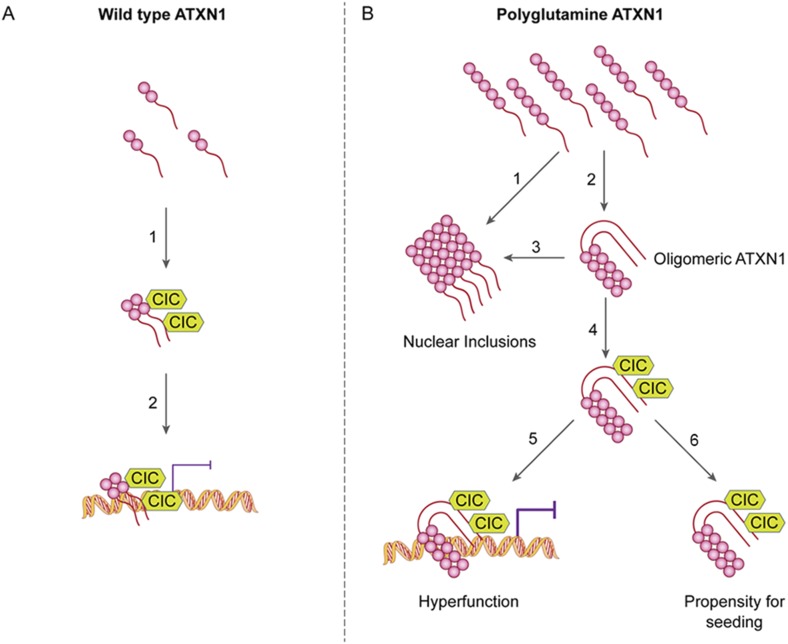
Figure 8. ATAXIN-1 oligomer complexes with seeding capability correlate with disease progression in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1: a model.
Under normal conditions (A, left panel), wild type ATXN1 forms a transcriptional repressor complex with CIC (1) and binds to DNA (2). Under pathological conditions (B, right panel), polyQ-expanded ATXN1 accumulates and can directly form nuclear inclusions (1) or it can adopt an oligomeric conformation (2). These oligomers form nuclear inclusions (3) or form a stable oligomeric complex with CIC (4) that could: act as a dysfunctional transcriptional repressor complex (5) or be released into the extracellular space and be internalized by neighboring neurons, seeding the formation of new oligomers (6). The toxic effect of oligomeric complexes might be mitigated by reducing the total levels of polyQ ATXN1 or hindering the propagation of these toxic complexes (e.g., by immunotherapy).