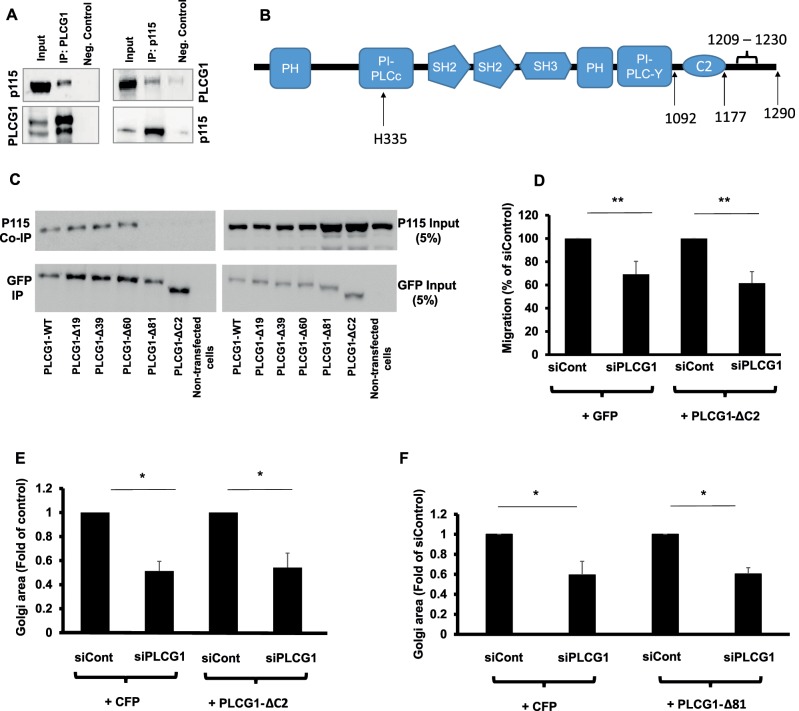
FIGURE 5:
(A) Coimmunoprecipitation of PLCG1 (IP: PLCG1) and p115 (IP: p115) from HeLa cell lysate. Input, the input material of the immunoprecipitation (5%). Neg. Control, the negative control in which the immunoprecipitation was performed in the absence of antibody but in the presence of protein G–Sepharose beads. Immunoprecipitated PLCG1 or p115 was eluted and immunoblotted against p115 and PLCG1, respectively (upper gel). Blots were stripped and immunoblotted against PLCG1 and p115 (lower gel). (B) Schematic depiction of the domains in PLCG1. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding wild-type GFP-tagged PLCG1 (PLCG1-WT) or truncation mutants lacking 19, 39, 60, and 81 C-terminal amino acids (PLCG1-Δ19, -Δ39, -Δ60, and -Δ81, respectively). In addition, a truncation mutant lacking the C2 domain was also used (PLCG1-ΔC2). After 24 h, cells were lysed and the lysate subjected to immunoprecipitation with GFP-tap beads (ChromoTek). The immunoprecipitated material was subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted against p115. The blot was stripped and probed with an antibody against GFP (to detect PLCG1). (D) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. After 48 h, cells were transfected with plasmids encoding either GFP or GFP-tagged PLCG1-ΔC2. After 8 h, cells were plated into ibidi migration inserts. Cell migration was initiated by removing the insert, and cells were allowed to migrate for 18 h. (E, F) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. After 48 h, cells were transfected with plasmids encoding GFP or GFP-tagged PLCG1-ΔC2 (E) or PLCG1-Δ81 (F). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from control (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01).