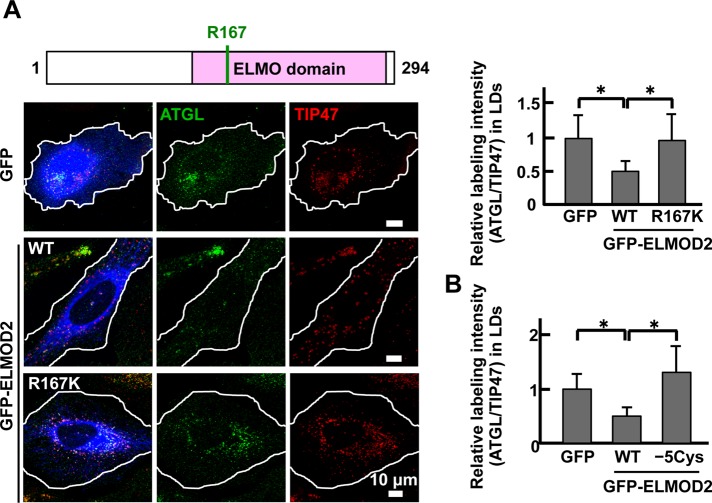
FIGURE 6:
ELMOD2 functionality and ATGL transport. (A) The effect of ELMOD2 expression on the amount of ATGL in LDs. After knockdown of endogenous ELMOD2 with RNAi, GFP cDNA or siRNA-resistant cDNA of either GFP-ELMOD2 (WT) or GFP-ELMOD2 (R167K) was transfected to HeLa cells. The cells were treated with 0.4 mM OA for 3 h and doubly labeled for ATGL (green) and TIP47 (red). In comparison with cells expressing GFP alone, the expression of GFP-ELMOD2 (WT) significantly decreased the relative labeling intensity of ATGL to TIP47 in LDs, whereas the expression of GFP-ELMOD2 (R167K) did not (mean ± SD; Student's t test; *p < 0.05). The results indicated that the Arf-GAP activity is indispensable for the effect of ELMOD2 on ATGL. The experiment was repeated three times, and 50 LDs chosen randomly from five micrographs were examined. (B) The same experiment as in A was performed to examine the effect of siRNA-resistant GFP-ELMOD2 (−5Cys). The expression of GFP-ELMOD2 (−5Cys) did not affect the relative labeling intensity of ATGL to TIP47, indicating that palmitoylation is critical for the functionality of ELMOD2 (mean ± SD; Student's t test; *p < 0.05). The experiment was repeated three times, and 100 LDs chosen randomly from 10 micrographs were examined.