Fig. 3.
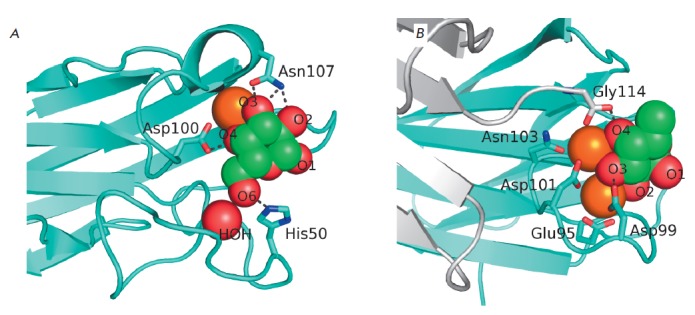
Detailed view of LecA (A) and LecB (B) sugar-binding sites. Lectins are shown as polypeptide chain trace models, where flat arrows indicate β-strands. Calcium ions are shown as orange spheres, and lectin-bound galactose and fucose are shown as green (carbon) and red (oxygen) spheres. The water molecule involved in galactose binding by LecA is shown as a red sphere, and the side chains of certain amino acid residues involved in sugar binding or calcium coordination are shown as sticks. Black dotted lines depict hydrogen bonds between the sugars and side chains of amino acid residues. The additional monomer of LecB is shown in gray (B); C-terminal glycine of this monomer is involved in the formation of the sugar-binding site of the neighboring monomer
