FIGURE 11.
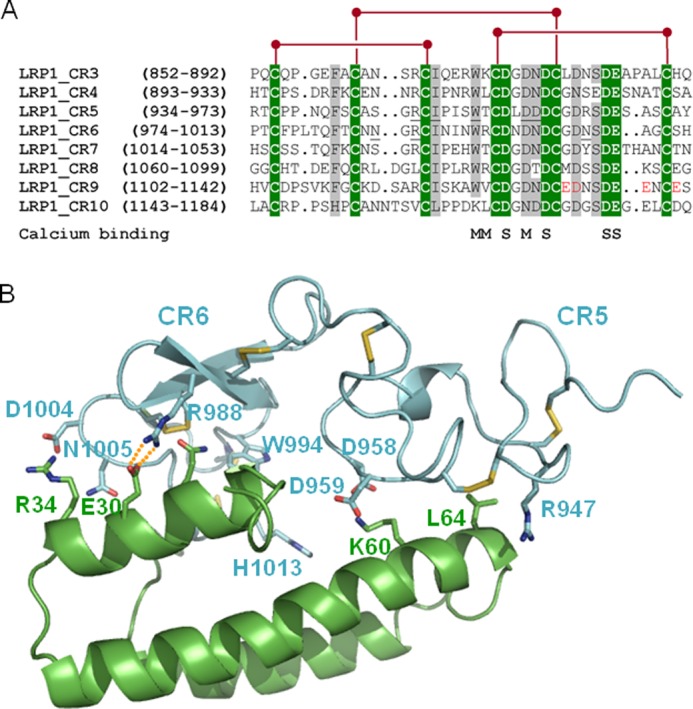
Common and unique sequence features of domain CR9. A, sequence alignment of CR modules from human LRP1 cluster II. Strictly conserved residues are white with green shading, and other well conserved or conservatively replaced residues are shaded gray. Disulfide bridges are shown above, and residues contributing main (M) or side chain oxygen atoms (S) to Ca2+ coordination are indicated below the alignment. Some residues from domains CR5 and CR6 involved in important interactions with RAP are underlined. The residues that form the unique acidic cluster in the C-terminal half of domain CR9 are highlighted in red. B, three-dimensional representation of the complex between the CR5 and CR6 repeats and RAP domain d1. LRP1 domains are given as a blue and RAP as a green schematic. Some interface residues are shown with all of their non-hydrogen atoms, color-coded. Note the presence of exposed salt bridges at the receptor-chaperone interface, in particular between Arg988 (CR6) and the acidic Glu30 in RAP.
