FIGURE 12.
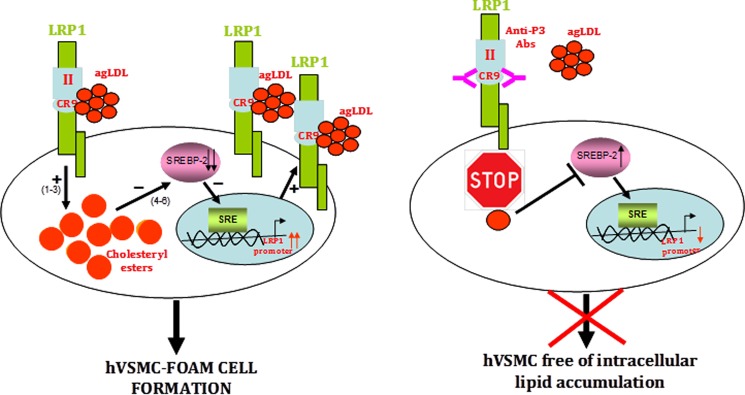
Schematic representation of the mechanism of AgLDL-mediated foam cell formation from human coronary VSMCs and modulation by anti-cluster II antibodies. The figure summarizes our current knowledge on the feedback loop of AgLDL uptake/LRP1 up-regulation/more AgLDL uptake that critically and efficiently contributes to foam cell formation from coronary hVSMCs. To the left, AgLDL are recognized by human VSMCs through LRP1 cluster II, with a particularly relevant role played by domain CR9. Uptake of bound AgLDL results in the accumulation of cholesteryl esters (1–3), which in turn causes the positive modulation of LRP1 promoter through SREBP-2 decay (4–6). To the right, antibodies directed to CR9 are able to interfere with the binding of aggregated LDL, thus effectively inhibiting downstream signaling events.
