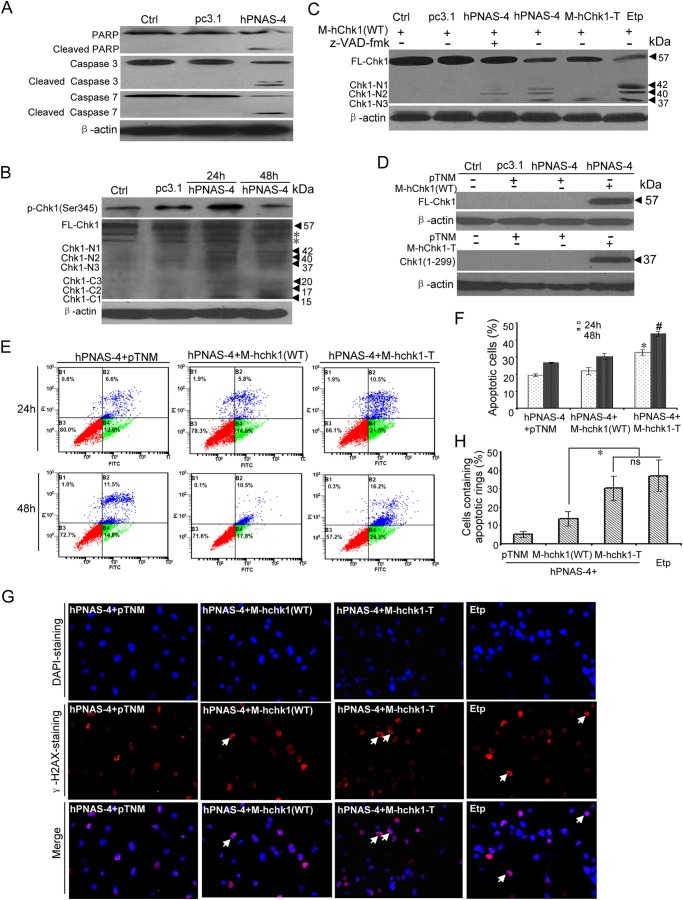
FIGURE 10.
Caspase-mediated cleavage of Chk1 contributes to PNAS-4-induced apoptosis. A, cleavage of caspase-3, caspase-7, and PARP during hPNAS-4-induced apoptosis. A549 cells were untreated or were transfected with pc3.1 or pc3.1-hPNAS-4 plasmid for 48 h, and then cleavage of caspase-3, caspase-7, and PARP was analyzed by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. B, time-dependent biphasic change of Chk1 phosphorylation and time-dependent cleavage of Chk1 during apoptosis. A549 cells were untreated or were transfected with pc3.1 or pc3.1-hPNAS-4 plasmid for 24 or 48 h, and then phosphorylated and cleaved Chk1 were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-Chk1 or anti-Chk1 antibody. FL-Chk1, full-length Chk1; Chk1-Nn, N-terminal cleavage fragments of Chk1; Chk1-Cn, C-terminal cleavage fragments of Chk1. β-Actin was used as a loading control. The asterisks indicate two nonspecific bands. C, caspase-dependent and -independent cleavage of Chk1 during apoptosis. A549 cells were transfected with M-hChk1(WT) plasmid for 48 h in the presence of 10 μm etoposide or co-transfected with M-hChk1(WT) and pc3.1, pc3.1-hPNAS-4, or M-hChk1-T plasmid for 48 h in the presence or absence of 10 μmol/liter benzyloxycarbonyl-VAD-fluoromethyl ketone (z-VAD-fmk), and then Chk1 truncation was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Myc antibody. FL-Chk1, full-length Chk1; Chk1-Nn, N-terminal cleavage fragments of Chk1. β-Actin was used as a loading control. D, overexpression of full-length Chk1 (WT) (top) and truncated Chk1 mimicking the N-terminal cleavage fragment (residues 1–299) (bottom) were confirmed by Western blotting with anti-Myc antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. E, truncated Chk1 mimicking the N-terminal cleavage fragment (residues 1–299) enhances PNAS-4-induced apoptosis. A549 cells were co-transfected with pc3.1-PNAS-4 and pTNM/pTNM-Chk1(WT)/pTNM-Chk1-T plasmids for 24 or 48 h. The treated cells were used for analysis of apoptosis by flow cytometry. F, quantification of apoptotic cells. A549 cells were treated as described in E, and then the percentage of apoptotic cells was counted. Bars, mean; error bars, S.D. (n = 3; *, p < 0.05; #, p < 0.05). G, formation of γ-H2AX apoptotic rings. A549 cells were co-transfected with pc3.1-PNAS-4 and pTNM/pTNM-Chk1(WT)/pTNM-Chk1-T plasmids for 48 h or treated with 10 μm etoposide for 12 h and fixed. Then cells were immunostained with anti-γ-H2AX (Ser-139) antibodies as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Arrows, typical γ-H2AX apoptotic rings. H, quantification of cells containing apoptotic rings. A549 cells were treated as described in G, and then the percentage of cells containing γ-H2AX apoptotic rings (at least 300 total cells) was counted. Bars, mean; error bars, S.D. (n = 3; *, p < 0.05; ns, not significant).