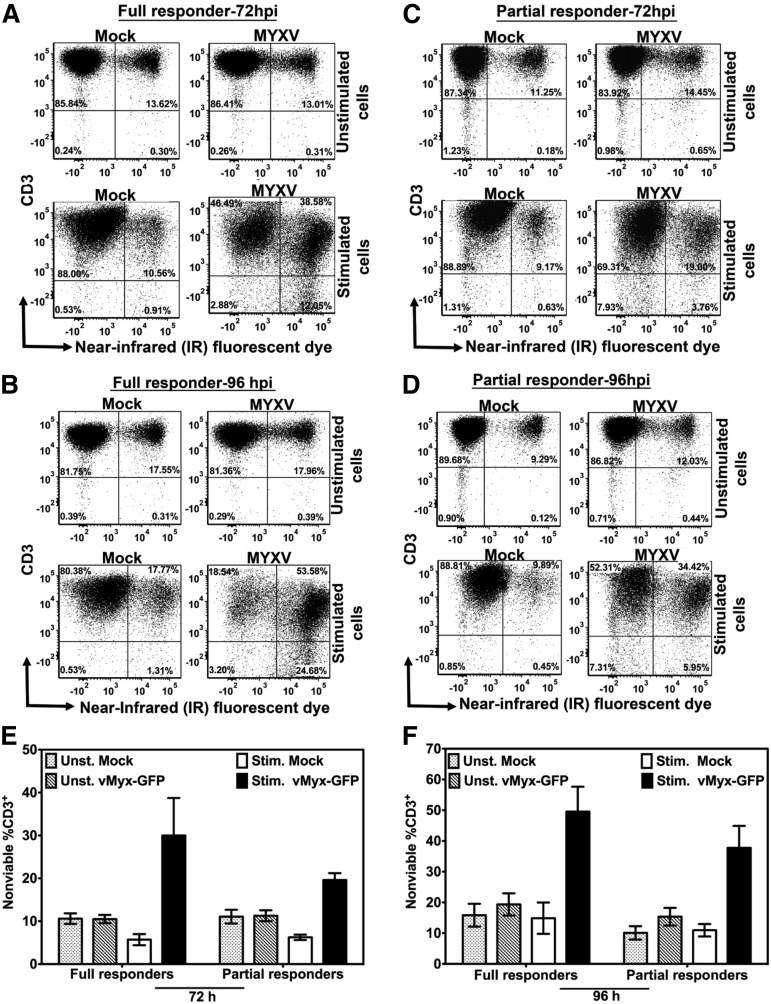
Figure 3.
MYXV infection and stimulation of human T cells reduces their viability. Cell death of T cells was evaluated 72 hours and 96 hours after mock-treatment or MYXV treatment, and ± anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation, using flow cytometry. To assess cell viability, T cells were labeled with the live/dead near-infrared (IR) fluorescent dye, an amine-reactive dye that binds covalently to intracellular and extracellular amines, generating a bright signal that allows the distinction between live/dead cells in a single channel. In addition, the staining pattern of this dye is preserved following cell fixation. (A-B) A representative full responder donor. (C-D) A representative partial responder donor. The percentage of cells was evaluated under unstimulated (top panels) and stimulated conditions (bottom panels). The data revealed that MYXV infection plus stimulation of T cells increased the percentage of cell death of the CD3+ population in culture. (E-F) Summaries of the profile of cell death among donors (N = 4 for each type of donor).