Figure 11.
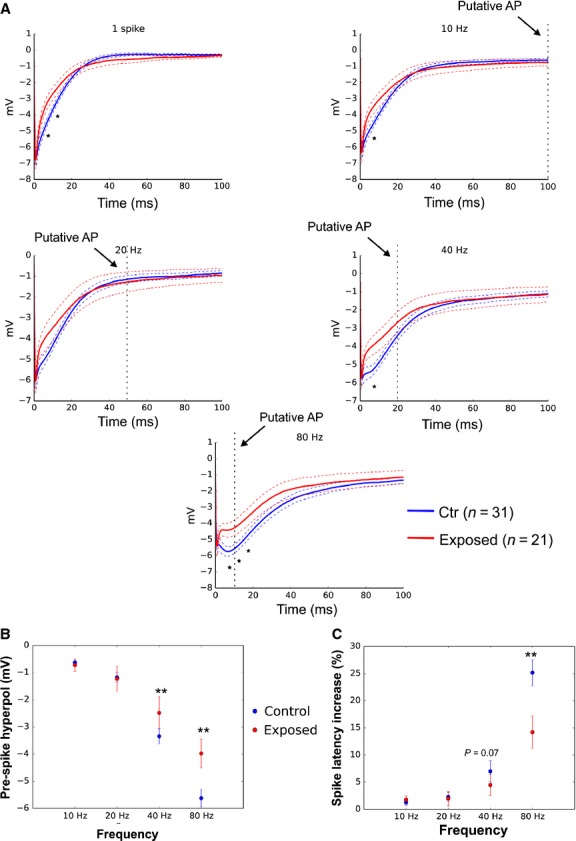
Odor exposure produces a reduction in the MC AHP limited to the range 5–20 msec postspike window. (A) Average traces of the AHP recorded at the end of the spike train in control (blue) and odor-exposed (red) animals. Thin dashed lines represent the SEM. Dashed vertical line depicts the occurrence of a putative spike for that specific frequency. It should be noted that the difference of the AHP between the two group can impact AP only when MC fire at high frequencies (B), The prespike hyperpol is significantly reduced in exposed animals when the MC firing frequencies was higher than 20 Hz. (C) As expected for lower prespike hyperpol the spike latency increase is reduced in exposed animals for frequencies higher than 40 Hz. Significantly difference between the two groups.*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
