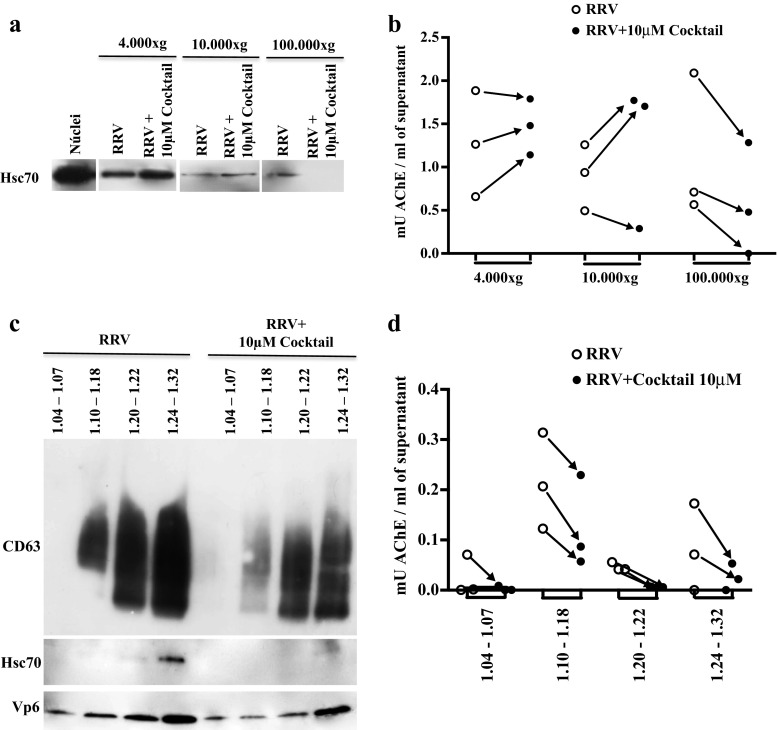
Fig. 3.
In Caco-2 cells infected with RV and pretreated with caspase inhibitors apoptotic bodies sediment at 100,000×g and float along the sucrose gradient. Caco-2 cells cultured for 15 days were treated with a caspase inhibitor cocktail (10 μM of z-VAD-fmk, z-DEVD-fmk, and z-LEHD-fmk) for 1 h and then infected with RRV (moi of five) or treated with the infection control (mock) for 45 min. The inhibitors were maintained during the virus inoculation and for 24 h after the infection. Subsequently, the supernatants of the treated cells were subjected to a differential centrifugation protocol: 300×g, 4000×g, 10,000×g, and 100,000×g to eliminate cellular debris and large vesicles of dead cells, microvesicles and exosomes, respectively. The EVs were evaluated by WB to identify the presence of the marker Hsc70 (a) and were quantified through the measurement of AChE activity per ml of supernatant (b). A representative image of three independent WB experiments is shown. EVs obtained by the filtration protocol were separated in a linear sucrose gradient at 100,000×g. The obtained fractions were grouped in the following manner according to their buoyancy density (g/ml): FG1 1.04–1.06, FG2 1.10–1.18, FG3 1.20–1.22, FG4 1.24–1.32. Left, WB evaluation of CD63, Hsc70, and VP6 (c). A representative image of three independent experiments is shown. Right, AChE quantification (d). The quantity (mU) of AChE present per ml of supernatant is shown