Figure 4.
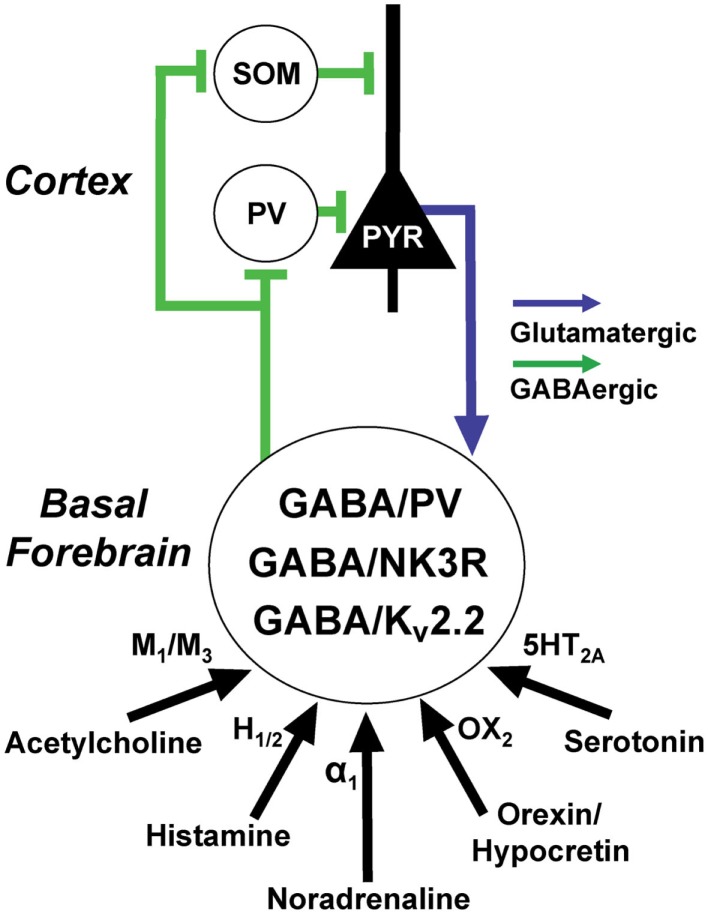
Basal forebrain (BF) GABAergic neurons are excited by wake promoting neuromodulators and promote gamma rhythms in the cortex via projections to cortical GABAergic interneurons. At least three, largely separate, populations of BF GABAergic neurons express the calcium-binding protein, parvalbumin (PV), the neurokinin-3 receptor (NK3R), and the potassium channel Kv2.2. BF GABAergic neurons can also be subdivided according to the amplitude and kinetics of their hyperpolarization-activated cation currents (H-currents). GABA/PV neurons in caudal/intermediate parts of the BF appear to be important in regulating cortical gamma oscillations through their synchronization of cortical PV interneurons. Rostral BF GABA/PV neurons (not shown) regulate hippocampal theta and gamma oscillations. The functions of the NK3R and Kv2.2. subpopulations are less well-understood but they also appear to be wake-promoting. Cortical and hippocampal projections of identified BF GABAergic or PV fibers preferentially appose GABAergic interneurons, including fast-spiking, somatic targeting PV interneurons, and dendrite-targeting somatostatin (SOM) interneurons. Return projections from the cortex target cortically projecting BF PV neurons and possibly other GABAergic subpopulations but avoid cholinergic neurons.