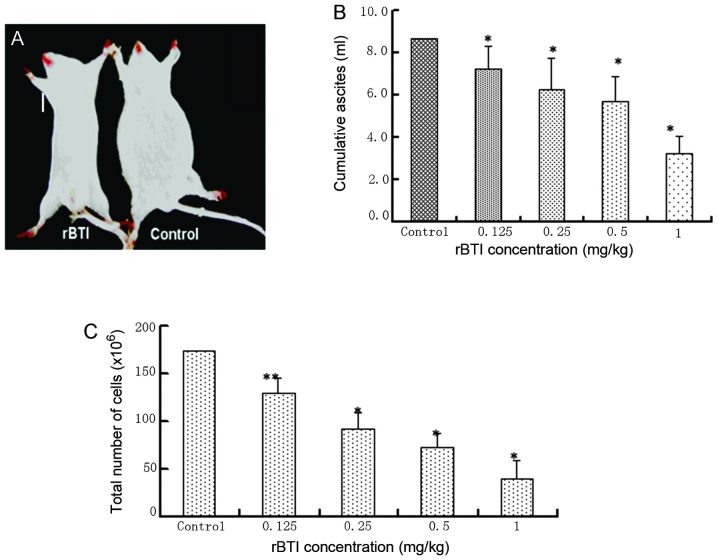
Figure 7.
Effect of rBTI on ascites and cancer cell development. Mice inoculated with H22 cells developed ascites and were then randomly assigned to either the control or rBTI treatment group (n=10 per group). (A) All mice in the control group developed overt ascites; however, no macroscopic signs of ascites formation was observed in the 1 mg/kg rBTI-treated mice. (B) The volume of ascites present was recorded. The volume of ascites collected in each animal from the initiation of the treatment was tallied up to provide the cumulative ascites volume. (C) Total number of viable H22 cells present in the ascites fluid (peritoneal wash) was counted using a hemocytometer. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with untreated cells. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of ten experiments. rBTI, recombinant buckwheat trypsin inhibitor.