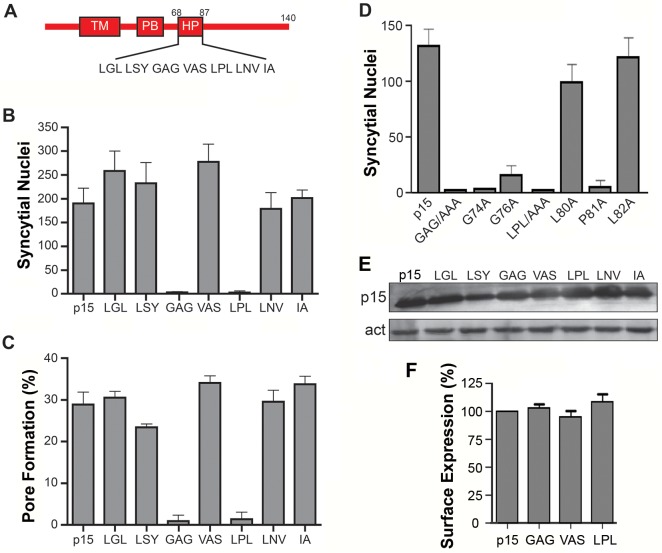
Fig 1. Centrally-located glycine and proline residues in the p15 HP are essential for cell-cell fusion.
(A) Schematic of the p15 protein indicating locations of the transmembrane domain (TM), polybasic cluster (PB) and hydrophobic patch (HP). Numbers indicate residue positions in p15. Sequence of the HP is depicted below. (B) Transfected QM5 cells expressing wt p15 or p15 mutant proteins containing triple Ala substitutions of the indicated three consecutive HP residues were Giemsa-stained at 9 h post-transfection and the mean ± SEM of syncytial nuclei per microscopic field were quantified by bright field microscopy. (C) QM5 cells co-transfected with EGFP and wt p15 or the indicated p15 HP mutant proteins as described in panel B were co-cultured with non-transfected cells labeled with calcein red, then sorted by flow cytometry to quantify the percentage of dual fluorescent cells indicative of pore formation. Results are the means ± SEM of Overton subtractions using duplicate samples from n = 2 independent experiments. (D) QM5 cells expressing wt p15 (p15) or p15 mutant proteins containing Ala substitutions of the indicated HP residues constructs were processed as in panel B to quantify syncytium formation. (E) Western blot of QM5 cell lysates expressing wt p15 or p15 mutant proteins containing triple Ala substitutions of the indicated HP residues HP were probed with anti-p15 antiserum and anti-actin. (F) Cell surface fluorescence of QM5 cells expressing wt p15 (p15) or p15 mutant proteins containing Ala substitutions of the indicated HP residues was quantified by flow cytometry using anti-p15 antiserum and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated secondary antibody. Results are percent surface fluorescence relative to wt p15. Bar graphs in panels B, D and E are the mean ± SEM for triplicate samples from n = 3 experiments.