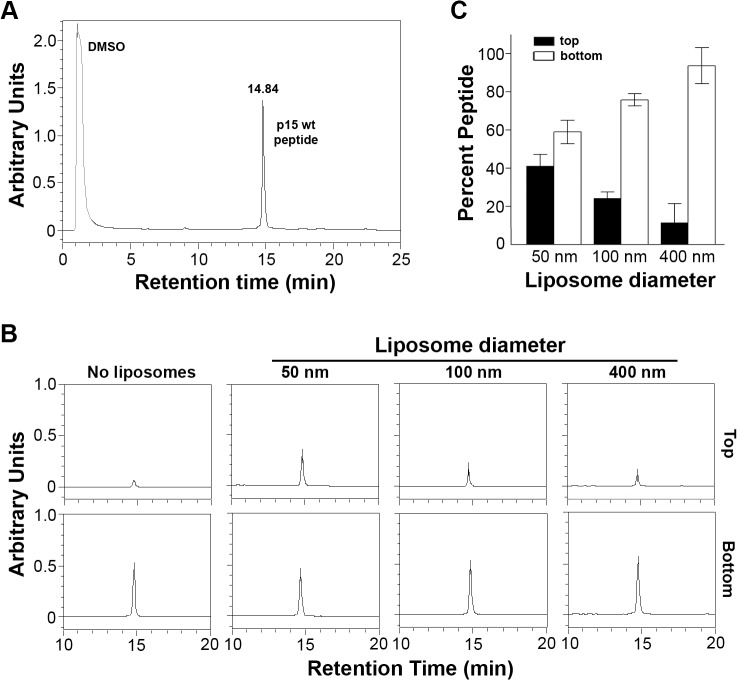
Fig 4. The p15HPpep peptide preferentially partitions into highly curved membranes.
(A) Purified wt p15HPpep dissolved in DMSO was resolved by reverse-phase HPLC using a water:acetonitrile gradient and eluted with the indicated retention time. The chromatogram presents the area under the peaks in arbitrary units of absorbance at 215 nm. (B) The wt p15HPpep was mixed with liposomes (1:1:1 DOPC:DOPE:cholesterol) of the indicated diameters at a fixed peptide:lipid molar ratio (1:500), and liposomes were separated from free peptide by flotation on sucrose gradients. The peptides present in the top liposome and bottom free peptide fractions were detected by HPLC. Chromatograms from a representative experiment are shown in arbitrary fluorescence units at the same scale for the retention time corresponding to the p15HPpep. The No Liposome chromatograms are for p15HPpep treated exactly as above but incubated in the absence of liposomes before sucrose gradient fractionation; the chromatogram indicates the low level of free peptide contaminating the top sucrose fraction. (C) The liposome (top) and free peptide (bottom) sucrose fractions were analyzed by HPLC as in panel B, and the relative peptide concentration in each fraction quantified by integrating the area under the peak in the HPLC chromatograms. Percent peptide = AreaTop / Total AreaTop+Bottom. Bars represent the mean SEM of three experiments.