Figure 4.
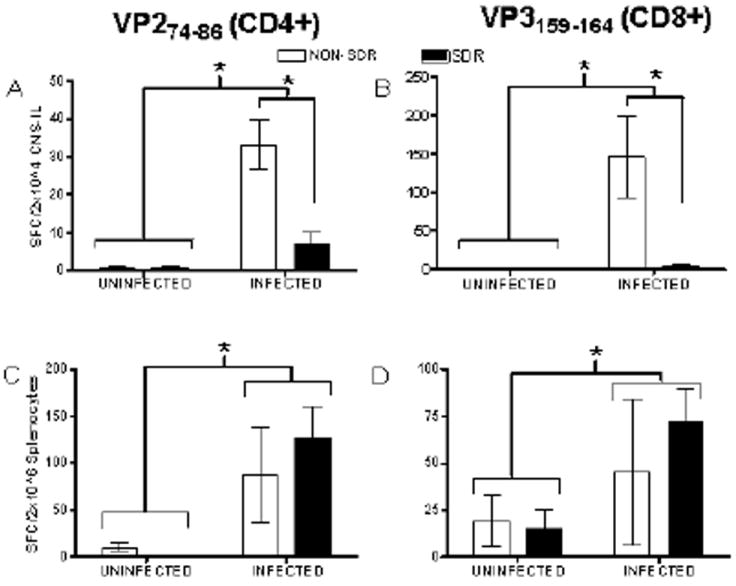
Data are presented as mean number of spot forming cells (SFCs) detected with IFN-γ detection antibodies (mean ± SEM) after SDR (or NON) and infection. Infection significantly increased the number of virus-specific CD4+ T cells (see Panel A) and virus-specific CD8+ T cells (see Panel B) detected in isolated CNS infiltrating lymphocytes (CNS-ILs; denoted by asterisk) while SDR exposure prior to infection prevented this increase (asterisk denotes significant difference between NON-SDR/Infected and SDR/Infected conditions). Infection significantly increased the number of virus-specific CD4+ T cells (see Panel C) and virus-specific CD8+ T cells (see Panel D) at day 8 post-infection (denoted by asterisk). SDR exposure did not significantly attenuate the elevation in either CD4+ or CD8+ T cells resulting from infection.
