Fig. 1.
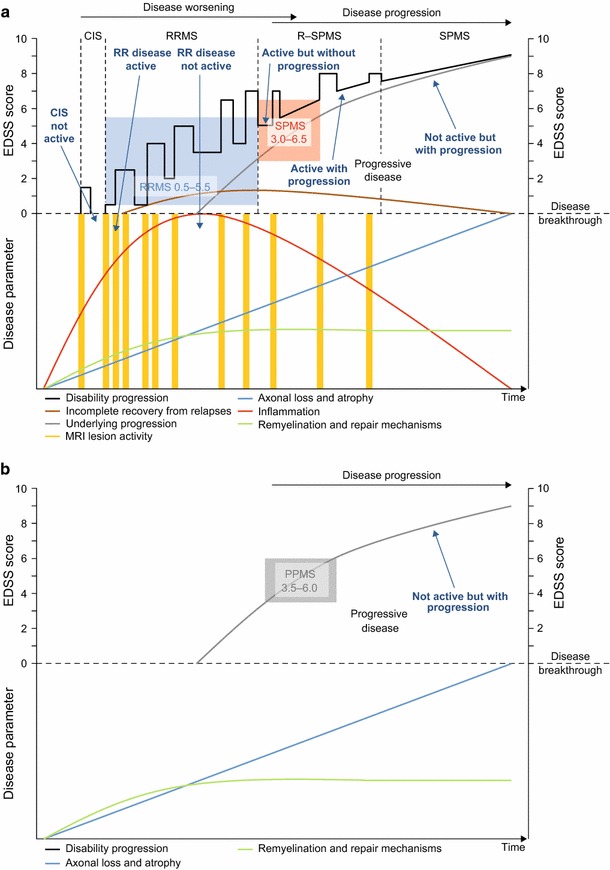
Schematic representation of the relationship between disability progression and the underlying pathological and rescue processes during a the typical relapsing–remitting disease course, which can ultimately transition into progressive disease, and b the purely progressive disease course. Disease worsening in patients with relapsing MS is a consequence of incomplete recovery from what is mostly focal inflammatory disease; disease progression is attributable to chronic diffuse neurodegenerative damage, a portion of which is caused by permanent focal damage. The colored boxes indicate typical eligibility criteria, as a range of EDSS scores, for recruitment into phase III trials. CIS clinically isolated syndrome, EDSS Expanded Disability Status Scale, MRI magnetic resonance imaging, MS multiple sclerosis, PPMS primary progressive MS, R–SPMS relapsing secondary progressive MS, RR relapsing–remitting, RRMS relapsing–remitting MS, SPMS secondary progressive MS
