Fig 10.2. Transcriptional regulation of Hepcidin.
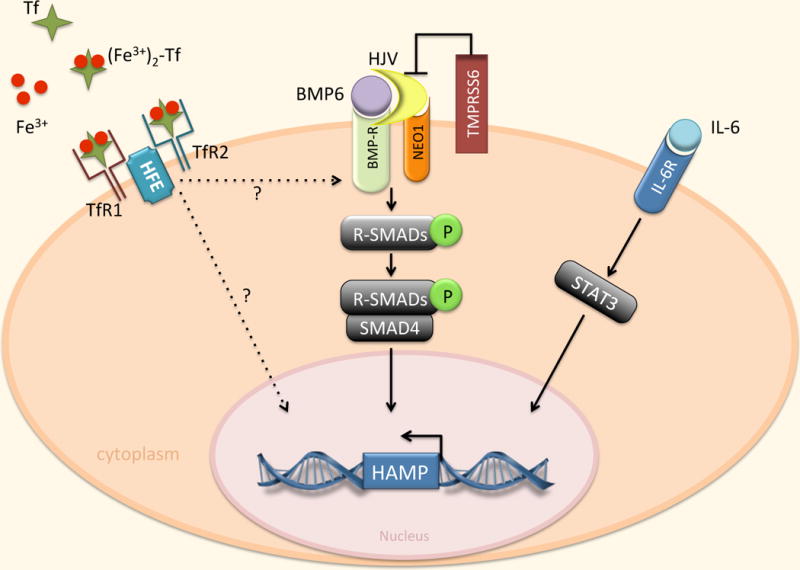
Regulation of hepcidin by BMP/SMAD and IL-6/STAT3 pathways. Expression of hepcidin in the liver is mainly affected by transcriptional mechanisms mediated by the BMP family, primarily BMP6. BMP binds to its receptor (BMPR) in conjunction with the co-receptor HJV. This interaction induces the phosphorylation of R-SMAD proteins which interact with the common mediator SMAD4, bind specific sequences in the hepcidin promoter, and trigger hepcidin gene (HAMP) transcription. NEO1 may enhance BMP signaling by interacting with HJV. TMPRSS6 negatively regulates hepcidin by cleaving HJV. Hepcidin expression is also induced by IL-6 through activation of STAT3. STAT3 binds to specific sequences in the HAMP promoter. TfR2 and HFE are also involved in hepcidin activation through mechanisms that are incompletely defined.
